Class 8 Science
Chapter 1 – Crop Production and Management
Very Important Questions Answers Set 3
Q.1. Which one of the following is not true about ploughing?
(a) It loosens the soil.
(b) It aerates the soil.
(c) It prevents soil erosion.
(d) It allows easy penetration of roots into the soil.
Ans: (c) It prevents soil erosion.
Ploughing refers to the loosening of the soil, which increases soil erosion. Loose soil can be easily washed off by water or carried away by wind.
Q.2. Compost lacks which of the following nutrients?
(a) nitrogen
(b) phosphorous
(c) potassium
(d) all of these
Ans: (d) all of these
Compost is made up of decomposed organic material. It is rich in organic nutrients but lacks nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium.
Q.3. Which one of the following does not add nutrients to the soil?
(a) crop rotation
(b) field fallow
(c) manures
(d) ploughing
Ans: (d) ploughing
Ploughing is a method to loosen the soil. It brings the soil that is rich in nutrients to the top from layers below, but does not add any nutrients to the soil.
Q.4. Which of these is not a cereal?
(a) maize
(b) gram
(c) wheat
(d) rice
Ans: (b) gram
Cereals, such as maize, wheat and rice, are tall grasses that are cultivated for grains. Gram is a pulse.
Q.5. Which of these is not a kharif crop?
(a) wheat
(b) rice
(c) maize
(d) groundnut
Ans: (a) wheat
Wheat is a rabi crop and is grown during the winter season (October to December).
Q.6. Which of these nutrients is compost rich in?
(a) organic nutrients
(b) nitrogen
(c) phosphorus
(d) potassium
Ans: (a) organic nutrients
Compost is made up of decomposed organic materials like dead plants and animal waste but it lacks nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium.
Q.7. Which of these is not a fungal disease of plants?
(a) wilt
(b) rust
(c) smut
(d) blight (of potatoes)
Ans: (a) wilt
Wilt is caused by bacterium. The bacterium grows in the xylem tissue of plants and blocks it. Thus, the xylem tissue becomes unable to transport water upwards and the plant wilts, eventually dying up.
Q.8. Which of the following machines can be used to harvest a crop and also to beat out the grain from the chaff?
(a) harvester
(b) combine
(c) thresher
(d) harrow
Ans: (b) combine
Combine is a farm machine that is used for harvesting and threshing.
Q.9. All crops require approximately the same amount of water at roughly the same time periods of their growth. True or false?
Ans: False. All crops require different amounts of water. For example, a paddy field needs more water compared to a wheat field.
Q.10. Pesticides are used to kill small pests, but they are not strong enough to harm humans. True or false?
Ans: False. Pesticides are harmful to our health. Fruits and vegetables must be washed before eating because they may be coated with pesticides.
Q.11. Some bacteria can convert nitrate salts in the soil to free nitrogen. True or false?
Ans: True. Some bacteria can convert nitrates present in the soil into free nitrogen by the process known as denitrification.
Q.12. Allowing a field to remain free of crops for one or more seasons is called field _________ It allows the field to regain _________
Ans: Allowing a field to remain free of crops for one or more seasons is called field fallow. It allows the field to regain nutrients.
Q.13. Large grasses cultivated for their nutritious seeds are called ________
Ans: Large grasses cultivated for their nutritious seeds are called cereals.
Q.14. Preparation of the soil involves _________ and _________ it.
Ans: Preparation of the soil involves loosening and turning it.
Q.15. The agricultural implement used to sow seeds is called a seed _________
Ans: The agricultural implement used to sow seeds is called a seed drill.
Q.16. Conversion of proteins into ammonia is called _________
Ans: Conversion of proteins into ammonia is called ammonification.
Q.17. A milch animal is one that yields __________
Ans: A milch animal is the one that yields milk.
Q.18. Rearing honeybees for honey is called __________.
Ans: Rearing honeybees for honey is called apiculture.
Q.19. If a crop is sown in June and harvested in October, what will it be classified as − rabi or kharif ?
Ans: A crop that is sown in June and harvested in October will be classified as a kharif crop.
Q.20. Name three crops that are classified as cereals and three that are classified as pulses.
Ans: Typical examples of cereals include paddy, wheat and maize. Some of the examples of pulses include peas, gram and beans.
Q.21. About how many years ago did agriculture begin?
Ans: Agriculture began about 10,000 years ago.
Q.22. Name one pesticide you will use to kill insects that harm crops.
Ans: Malathion is a pesticide that is used to kill insects that harm crops.
Q.23. Name the nitrogen fixing bacteria in root nodules of leguminous plants.
Ans: Rhizobium is a nitrogen fixing bacterium that is found in the root nodules of leguminous plants.
Q.24. Name three natural methods of adding nutrients to soil.
Ans: The three natural methods of adding nutrients to soil are:
Field fallow
Crop rotation
Mixed cropping
Q.25. What are weeds?
Ans: The unwanted plants that grow along with the crops are called weeds. Weeds decrease the crop yield as they compete with crops for water, nutrients and sunlight and limit their growth.
Q.26. It is necessary to loosen the soil by ploughing before sowing seeds. Why is it necessary to level the soil after ploughing?
Ans: After ploughing, the soil may still contain large lumps of soil. These lumps of soil are crushed through the process of levelling. Moreover, levelling also reduces the chances of soil erosion.
Q.27. Seeds are often grown in nurseries and then transplanted to the fields. What is the advantage of this?
Ans: Some crop plants such as tomatoes, rice and onion are planted into seed beds called nurseries. These plants are allowed to develop into seedlings, which are then transplanted to the field. This allows farmers to select healthy seedlings; thereby, increasing crop production.
Q.28. Which of these are organic substances−manures or fertilizers?
Ans: Manures are considered as organic substances because they are derived from the decomposition of dead animals and plants. Fertilizers, on the other hand, are inorganic substances derived from chemicals.
Q.29. Drip irrigation saves wastage of water because it supplies water directly to the roots. Why is drip irrigation not used by all farmers?
Ans: Drip irrigation is used to supply water directly near the roots of the plants through a pipe. This process is extremely beneficial in areas of water shortage. However, this process is very expensive and thus, most of the farmers do not use drip irrigation.
Q.30. Some fruits such as grapes are not peeled before eating. You are advised to be extra careful in cleaning such fruits. Why?
Ans: Fruits and vegetables are generally grown with the help of chemical pesticides, which are extremely harmful for human health. In case of fruits that are not peeled, a coating of pesticide may still even remain after through washing. It is therefore advised that such fruits should be carefully cleaned.
Q.31. After harvesting his bountiful crop, a farmer was so happy that he forgot to dry the crop before storing it. What problems can he face?
Ans: The drying of crops is essential to prevent the growth of microbes. The farmer in the given case, has not dried the crop and thus, his crops will have high amount of moisture. This high moisture will lead to the growth of microbes and consequently, food grains will be spoilt during storage.
Q.32. A farmer has two varieties of wheat in his field−one gives good yield but is prone to diseases; the other is resistant to diseases but does not give good yield. How can you help him as an agriculture scientist?
Ans: In the given case, two varieties of wheat are available. One of the varieties of wheat is prone to diseases but gives a good yield. Another variety of wheat is disease resistant but provides a good yield. As an agriculture scientist, one could recommend that the two varieties should be hybridised to obtain a hybrid. This hybrid would have disease resistance and will provide high yield.
Q.33. Which one of these add nitrogen in usable form to the soil−nitrifying bacteria or denitrifying bacteria?
Ans: Nitrifying bacteria convert ammonia into nitrate compounds, which are readily utilised by the plants. Denitrifying bacteria, on the other hand, convert nitrates into free nitrogen, which cannot be used by the plants. Thus, nitrifying bacteria add nitrogen in usable form to the soil.
Q.34. If you are a pisciculturist, what do you do?
Ans: A pisciculturist is involved in the large-scale production and rearing of fishes.
Q.35. If you say that a certain process 'fixes nitrogen' what does this mean? Which natural process in the atmosphere fixes nitrogen?
Ans: Nitrogen fixation is the process in which atmospheric nitrogen (gaseous nitrogen) is converted into nitrogen compounds. These nitrogen compounds are then utilised by the living organisms. In atmosphere, lightening generates high temperatures, which leads to the reaction of oxygen and nitrogen to produce nitrogen oxides. This process is responsible for natural fixation of nitrogen.
Q.36. Why should grains be dried before storage?
Ans: Grains should be dried before storage because they contain moisture. This excess moisture promotes microbial growth that may destroy the grains.
Q.37. Why does the government usually maintain a buffer stock of grains?
Ans: The government usually maintains a buffer stock of grains to avoid shortage of grains that might result from a decrease in the production or a natural disaster.
Q.38. What is hybridisation?
Ans: Hybridisation can be defined as a technique to develop new varieties of crops by cross-breeding two different parental varieties.
Q.39. List the steps involved in the nitrogen cycle.
Ans: The steps involved in the nitrogen cycle are as follows:
Nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen assimilation
Ammonification
Nitrification
Denitrification
Q.40. What do you mean by nitrogen fixation?
Ans: Nitrogen fixation is the process of converting free nitrogen gas present in the atmosphere into nitrogen compounds that can be absorbed by the plants.
Q.41. What is nitrogen assimilation?
Ans: Nitrogen assimilation is the process by which inorganic nitrogen compounds are converted into organic compounds such as proteins that become a part of living beings.
Q.42. What enables leguminous plants to fix nitrogen?
Ans: The nitrogen-fixing bacterium called Rhizobium that live in the root nodules of leguminous plants enables them to fix nitrogen.
Q.43. What is animal husbandry?
Ans: Animal husbandry is defined as the feeding, breeding, rearing and caring of domestic animals so as to obtain food and other products from them.
Q.44. Why is it important to plant seeds at the correct distances from each other?
Ans: Seeds should be planted at a proper distance from each other because if they are very near to each other, they will compete for water, nutrients and sunlight. If they are far apart, they will take up a large area, resulting in the wastage of field space.
Q.45. Why do farmers normally use a mixture of manure and fertilizers in their fields?
Ans: Farmers normally use a mixture of manure and fertilizers in their fields to increase the yield and production of crops. Manure is good for plants as it provides them with organic nutrients but it lacks some important nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium. So, along with manure, farmers also use fertilizers such as NPK fertilizers that provide nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium.
Q.46. What method of irrigation will you use if you live in a dry area with shortage of water? Explain the method.
Ans: Drip irrigation is the method of choice for dry areas which have a shortage of water.
In this method, water is directed at the roots of plants. Water is allowed to fall drop by drop from a pipe placed near the roots. Thus, water is used efficiently and wastage is reduced.
Q.47. What is waterlogging? How does it harm the crops? How can it be prevented?
Ans: Water logging is caused when an excess of water is supplied to the field and it replaces the air present in the pores of the soil. As a result of this, the air supply to the roots reduces and in extreme cases, gets totally cut off. This results in the retarded growth of plants. Water logging can be prevented by supplying just the adequate amount of water to the field using a proper drainage system.
Q.48. Discuss two methods of weeding in which poisonous chemicals are not used.
Ans: The two methods of weeding in which chemicals are not used are:
Manual method: Weeds are pulled out by hand or uprooted using a trowel or a harrow.
Insect method: Insects that feed upon specific weeds are used.
Q.49. Differentiate between insecticides, rodenticides and fungicides. Which of these are pesticides?
Ans:
|
Insecticides |
Rodenticides |
Fungicides |
|
Insecticides are chemicals used to kill insects like locusts. |
Rodenticides are chemicals used to kill rodents like rats. |
Fungicides are chemicals used to destroy fungi. |
Insects, rodents and fungi are pests. So, insecticides, rodenticides and fungicides are all pesticides.
Q.50. Discuss with an example how hybridization is used for developing new varieties of crops with desired characteristics.
Ans: Hybridization involves cross-breeding two different varieties of crops to obtain a new variety with the desired traits.
Example: Two varieties of crops, one with high yield and other with disease resistance, can be crossbred to obtain a variety that has both the traits, i.e., high yield and disease resistance.
Q.51. Differentiate between nitrification and denitrification.
Ans:
|
Nitrification |
Denitrification |
|
It is the process of conversion of ammonia into nitrates. |
It is the process of conversion of nitrates into free nitrogen gas. |
|
It is carried out by nitrifying bacteria. |
It is carried out by denitrifying bacteria. |
Q.52. What are the advantages of ploughing the soil before sowing seeds?
Ans: Ploughing the soil before sowing seeds have the following advantages:
Ploughing loosens and mixes the soil. During ploughing, an adequate amount of air gets trapped in the pores of the loosened soil. Plant roots use this air to breathe.
Plant roots can penetrate deeper in loose soil and thus hold the plant firmly.
Loose soil is good for the growth of earthworms and microbes that provide nutrients to the soil and help in further loosening it.
During ploughing, the nutrient-rich soil is brought to the top. Thus, plants can absorb the nutrients more easily.
Loose soil mixes well and uniformly with the added fertilisers.
Q.53. What precautions must be taken while sowing seeds in a field?
Ans: While sowing seeds in a field, the following points must be kept in mind:
Seeds of good quality and health should be selected.
Seeds must be planted at the proper depth in the soil.
Water is required for the germination of seeds. Therefore, the soil must have adequate water in it.
Seeds should be sown at a proper distance from each other. If they are sown very close, they will compete for water, sunlight and nutrients. If they are sown too far away, it will result in the wastage of field area.
Q.54. Discuss two natural methods of manuring.
Ans: Two natural methods of manuring are:
Field fallow: In this method, the land is left free or fallow for one or more seasons. This allows the land to naturally regain nutrients. Microbes decompose dead plants, animal waste and other organic material that get collected in the land. Thus, the soil regains the lost nutrients.
Crop rotation: Different crops require different nutrients. Therefore, farmers plant different crops each season. This is called crop rotation. It prevents depletion of nutrients in the soil.
Q.55. Which method, according to you, can lead to maximum increase in crop produce in our country in future?
(a) increasing land under cultivation
(b) using more manures and fertilisers
(c) less wastage in storage
(d) using better varieties of crop plants
Ans: (d) using better varieties of crop plants.
Using better varieties of crop plants will result in increased production. Plant breeding is the method of choice to develop better varieties that have a higher yield as well as high resistance to diseases.
Q.56. What do you think are the drawbacks of uneven distribution of seeds in a field while sowing?
Ans: The drawbacks of uneven distribution of seeds in a field, while sowing, are:
(i) If seeds are sown very close to each other, they will compete for water, nutrients and sunlight. This will limit their growth.
(ii) If they are sown far apart, it will result in the wastage of field area.
(iii) If seeds are not sown at the proper depth and covered by soil, they may be eaten up by birds.
Q.57. Do you expect to find fully-grown crop plants in a nursery? Why? Why not?
Ans: We won't find fully-grown crop plants in a nursery. Nurseries are seed beds in which the seeds of some crops like rice, tomato, onion, etc. are sown. When these seeds grow into seedlings, they are transferred to and planted in the fields. Thus, in a nursery, fully-grown crops are not present, as they are transferred to the fields from nurseries in their seedling stage.
Q.58. Crop rotation is practised by farmers so that they have different products to sell in the market in every season. Do you agree? Give reasons.
Ans: No, farmers do not adopt crop rotation to sell different products in the market every season. They adopt crop rotation to maintain the balance of nutrients in the soil.
Different crops require different nutrients. Some crops may require more of some particular nutrients and less of others. Therefore, farmers plant different crops each season to prevent the depletion of nutrients in the soil.
Example: Wheat absorbs nitrogen present in the soil. The amount of nitrogen can be naturally replenished if farmers grow legume crops the subsequent season. The nitrogen-fixing bacterium Rhizobium, present in the root nodules of leguminous plants, helps in fixing atmospheric nitrogen. Thus, the soil is prepared for planting wheat the following season.
Q.59. I have grown a few wheat plants in my garden because I like the plants. Am I growing a wheat crop? Give reasons.
Ans: No. Growing a few plants in a garden is not crop production. Crop production is growing wheat in a field on a large scale to cultivate grains.
Q.60. It is observed that melon fruits growing in the fields sometimes crack, exposing the contents inside. What do you think can be the reason? (HINT: This generally happens in fields without proper drainage.)
Ans: Melons growing in waterlogged fields with poor drainage tend to absorb more water than they require. Melons cannot hold this excess water; therefore, they crack.
Q.61. Mohan and Sohan are farmers in Rajasthan, where there is shortage of water. Mohan waters his crops through irrigation channels connected to a tube well. Sohan uses drip irrigation. Which of them shows greater concern for the environment?
Ans: Sohan shows greater concern for the environment by using drip irrigation for watering his crops. Drip irrigation allows water to fall drop by drop near the roots of the plants and thus reduce the wastage of water. However, use of irrigation channels for watering the crops leads to a lot of wastage of water.
Q.62. Agriculture deals with plants and not with animals. Do you agree? Give reasons.
Ans: Agriculture can be defined as the science of rearing animals and growing crops to meet the demands of humans. The concept of agriculture utilises different methods to improve the overall yield of the crops. Moreover, agriculture also focuses on improving the quality as well as quantity of animal products by following scientific procedures. Thus, the given statement is incorrect.
Q.63. Distinguish between kharif and rabi crops, giving two examples of each.
Ans:
|
Kharif crops |
Rabi crops |
|
They are sown at the beginning of the south-west monsoon i.e., during June or July. |
They are sown at the beginning of winter i.e., from October to December. |
|
They are harvested in September or October after the monsoon season. |
They are harvested in March or April. |
|
Examples: rice, maize |
Examples: wheat, pea |
Q.64. List the steps involved in crop production, in sequential order.
Ans: The steps involved in crop production are as follows:
Preparation of soil
Seed selection and sowing
Manuring, irrigation and weeding
Protection from pests and diseases
Harvesting, threshing and winnowing
Storage
Q.65. An experiment was conducted to study the effect of a new fertilizer on the growth of two varieties of wheat. The data for growth of the plants from germination to next 10 days is shown in the figure.
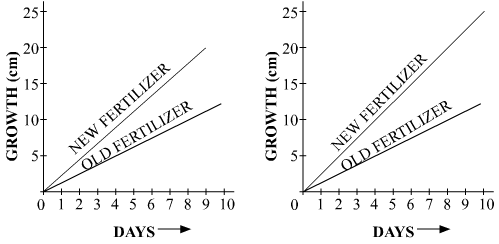
All other growing conditions such as water and sunlight were kept the same for both the varieties.
Which of the following is the most reasonable conclusion you can draw from the data?
1. The new fertilizer causes faster growth in both varieties than other fertilizers.
2. The new fertilizer causes faster growth in both varieties in the first ten days only.
3. The new fertilizer influences the growth of both varieties.
4. The new fertilizer causes faster growth in variety B than in Variety A.
Ans: Let’s consider the first graph showing the effect of fertiliser on growth of variety A and first graph showing the effect of fertiliser on growth of variety B.
From the above graph we can see that, the new fertiliser causes faster growth in variety B than in variety A.
Q.66. Draw a labelled diagram to illustrate the nitrogen cycle.
Ans: Nitrogen cycle is a process in which atmospheric nitrogen is fixed, then used by plants and animals and finally returned to the atmosphere.

NITROGEN CYCLE
Online Tuitions & Self-Study Courses for Grade 6 to 12 & JEE / NEET
