Class 7 Science
Chapter 2 – Nutrition in Animals
Important Questions Answers – Set 2
Q.1. Small intestine in herbivores is longer than in carnivores. Do you agree? Support your answer.
Ans. Yes, carnivore animals cannot digest cellulose, hence they have a shorter small intestine.
In herbivores, digestion of cellulose takes a longer time. Hence, herbivores need a longer small intestine to allow complete digestion of cellulose.
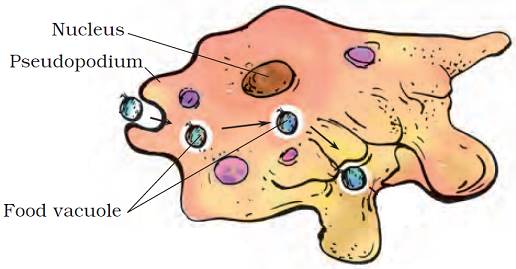
Q.2. Draw a neat and clean diagram of Amoeba showing the correct location of the following components : nucleus, vacuole, pseudopodia.
Ans.
Q.3. Draw the labelled diagram of tongue showing different region for taste buds.
Ans.

Q.4. Ruminants such as cows and buffaloes swallow their food hurriedly and then sit restfully and chew their food. Give reason.
Ans. Ruminants such as cows and buffaloes swallow their food hurriedly and store it in a part of the stomach called rumen. The cellulose of the food is digested here by the action of certain bacteria which are not present in humans. Later, this partially digested food is returned to the buccal cavity of the animals in small lumps and animal chews it to complete the process of digestion. This process is called rumination.
Q.5. Discuss the position and number of molars in buccal cavity.
Ans. Molars are very large teeth which are present behind the premolar, towards the back of our mouth. They are only present in the permanent set of teeth and are 6 in each jaw.
Q.6. Name the three digestive glands in our body.
Ans. The three digestive glands are
(i) Liver
(ii) Pancreas
(iii) Salivary glands
Q.7. The swallowed food moves downwards in the alimentary canal. Explain.
Ans. The swallowed food moves downwards in the alimentary canal because of the alternate relaxation contraction movement of muscles in the wall of food-pipe called peristalsis.
Q.8. Explain how assimilation is different from absorption.
Ans. The process by which nutrients from the digested food are absorbed by the body is called absorption whereas the process by which the absorbed nutrients are utilised by the body for providing energy is called assimilation.
Q.9. Food moves in the opposite direction during vomiting. How?
Ans. The intense pressure is formed in the stomach when the food is not accepted by the stomach. The content in the stomach is then pushed back. This returned content is expelled out from the mouth in the form of vomiting.
Q.10. Briefly explain, why animals like cow cannot chew their food properly at the time they take it in.
Ans. Animals like cow cannot chew their food properly due to the presence of cellulose in their diet. At the time they take in food, the food is moistened and is sent for cellulose digestion and softening in rumen.
Q.11. Is there any role of liver in digestion of fats? Explain.
Ans. Yes, liver produces bile which has bile salts. These salts break large fat molecules to fine droplets. These fine droplets are further converted into fatty acids and glycerol.
Q.12. Cellulose rich food substances are good source of roughage in human beings. Justify.
Ans. Cellulose rich food substances are good source of roughage in human beings. It is because the cellulose digesting bacteria are not present in the body of human beings due to which human beings cannot digest cellulose (present in plant foods).
Q.13. Recall and name the main organs of the digestive system in our body.
Ans. The different organs of the alimentary canal are as follows:
(i) Mouth and mouth cavity
(ii) Oesophagus
(iii) Stomach
(iv) Small intestine
(v) Large intestine
(vi) Anus
Q.14. Alimentary canal is different from digestive system. Comment.
Ans. Alimentary canal is a long, muscular coiled tube. It is also known as digestive tract. The alimentary canal with its associated glands constitutes the digestive system. These glands are salivary glands, liver and pancreas.
Q.15. Windpipe runs adjacent to the food-pipe. What will happen if food particles enter the windpipe? Explain.
Ans. The windpipe carries air from the nostrils to the lungs. It runs adjacent to the food-pipe. If, by chance, food particles enter the windpipe, we feel choked, get hiccups or cough.
Q.16. Explain how is small intestine designed to absorb digested food.
Ans. The finger-like projections called villi are present in the inner walls of the small intestine. The villi increase the surface area. The large surface area of small intestine helps in the rapid absorption of the digested food .
Q.17.
(a) What is hiccup?
(b) Why do we get hiccup?
Ans.
(a) Hiccup is a choking sensation that produces a characteristic gulping sound repeatedly.
(b) Sometimes, when we eat too fast in a hurry or talk too much or laugh while eating, then a little of windpipe remains open due to which food particles may enter the windpipe. It may result in a choking sensation called hiccups.
Q.18.
(a) Name the term used to describe the condition in which a person passes out watery stools.
(b) Name the solution of sugar and salt in water. Why is it given to a person suffering from diarrhoea?
Ans.
(a) Diarrhoea.
(b) Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS). It is given to a person suffering from diarrhoea to prevent the dehydration.
Q.19. Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow it.
Bile juice is stored in a sac called, gall bladder, located near its organ of secretion, liver. The gall bladder releases the bile juice into the small intestine whenever food reaches there. Though bile juice is devoid of any digestive enzymes, it is required for the digestion of fats. The fats cannot be digested easily because they are insoluble in water and are present as large globules. Bile juice breaks down big fat droplets into smaller droplets. These are then easily digested by the enzymes released from the pancreas
(a) Which organ secretes the bile juice?
(b) Why is digestion of fats difficult as compared to that of other nutrients?
(c) How does bile juice help in digestion of that of other nutrients?
(d) Where is the digestion of fat completed?
(e) Does bile juice digest fat completely?
Ans.
(a) Bile juice is secreted by liver.
(b) Digestion of fats is difficult as compared to that of other nutrients because of insolubility of fat in water.
(c) Bile juice helps in digestion of fat by breaking down big fat droplets into smaller droplet.
(d) Digestion of fat is completed in small intestine.
(e) No, fat is not completely digested by bile juice.
Q.20. Define oral rehydration solution and when it is given to the patient? How can you prepare ORS at home?
Ans. Oral rehydration solution is the solution of sugar and salt in a particular ratio in the clean water. When a person passes out watery stools frequently, the disease is called diarrhoea. In this condition there is a loss of water and salt from the body of a person. This is called dehydration which may be fatal if not cured at proper time. In order to prevent dehydration, the person or patient should be given ORS. ORS makes up the loss of water and salts in the body and sugar provides energy which helps in the recovery of disease. it should be given to a patient suffering from diarrhoea at a regular interval.
At home the ORS can be prepared by dissolving a teaspoonful of sugar and pinch of salt in a glass of clean water. The water used for preparing ORS should be first boiled and then cooled so that all the microorganisms or harmful bacteria may be killed.
Q.21. Explain how the digestion of cellulose occurs in grass eating animals.
Ans. Grass eating animals quickly swallow the grass and store it in a part of stomach called rumen. The food is not chewed completely.
Rumen possess cellulose digesting bacteria which breakdown the food by fermentation. This partially digested food or grass present in the rumen of cow is called cud.
This cud is brought back into the mouth of the cow from the rumen into small lumps and animal chews it again.
This process is called rumination and animals are called ruminants.
When this cud is thoroughly' chewed in the mouth of the cow, it is swallowed again. This time the chewed cud does not go back to rumen but enter into the other compartments of cow's stomach and then into the small intestine for complete digestion and absorption of food.
Q.22. Label the given figure as directed below in A to D and give the name of each type of teeth.
(a) The cutting and biting teeth as A
(b) The piercing and tearing teeth as 8
(c) The grinding and chewing teeth as C
(d) The grinding teeth present only in adult as D

Ans.

Q.23. Briefly describe the process of digestion in Amoeba with the help of labelled diagram.
Ans. The food of Amoeba are microscopic organisms like tiny plants and animals present in pond water.
When Amoeba senses its food, it pushes out pseudopodia around the food particle and engulfs it.
The two pseudopodia join around the food particle and trap the food particle with a little water forming vacuole around food, thus the food gets trapped.
Digestive juices present inside the vacuole, acts on the food and break it into simpler substances.
This digested food is then absorbed and is used for growth, maintenance and multiplication of Amoeba.
The undigested food residue is expelled outside by the vacuole.

Q.24. Label the following parts of the given figure and name them.
(a) The largest gland in our body.
(b) The organ where protein digestion starts.
(c) The organ that releases digestive juice into the small intestine.
(d) The organ where bile juice gets stored.

Ans.

Online Tuitions & Self-Study Courses for Grade 6 to 12 & JEE / NEET
