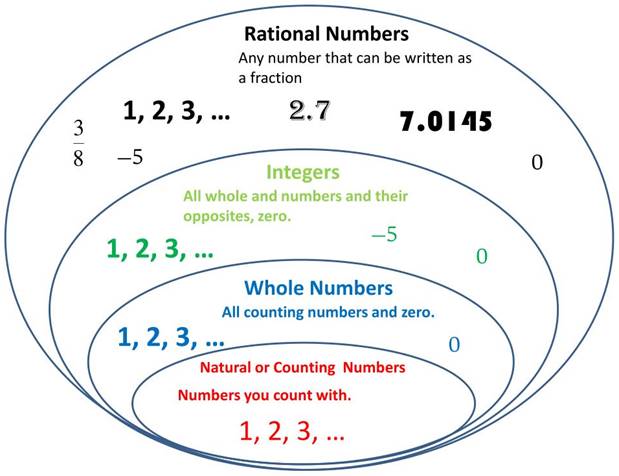
Rational Numbers
Rational Numbers are the numbers that can be expressed in the form p/q where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0.
Rational numbers include all natural numbers, whole numbers, fractions and integers.
Equivalent Rational Numbers
By multiplying or dividing the numerator and denominator of a rational number by the same integer, we can obtain another rational number equivalent to the given rational number.
Numbers are said to be equivalent if they are proportionate to each other.
Example

Therefore −2/3 and 10/(−15) are equivalent to each other as they are equal to each other.
Positive and Negative Rational Numbers
1. Positive Rational Numbers are the numbers, whose both the numerator and denominator are either positive or negative.
Example: 3/4, 12/24 etc.
2. Negative Rational Numbers are the numbers whose one of the numerator or denominator is negative.
Example: (−2)/6, 36/(−3) etc.
Remark: The number 0 is neither a positive nor a negative rational number.
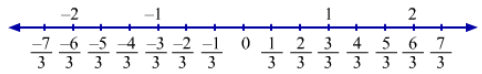
Rational Numbers on the Number Line
Positive rational numbers are on the right to 0 and negative rational numbers are on the left of 0.
Representation of rational numbers can be done on a number line as follows
Rational Numbers in Standard Form
A rational number is in the standard form if
~ its denominator is a positive integer
~ there is no common factor between the numerator and denominator other than 1
We can reduce a rational number to its standard form or the lowest form by dividing its numerator and denominator by their HCF ignoring its negative sign.
Example
Find the standard form of 18/24.
Solution
![]()
3/4 is the standard or simplest form of 18/24.
Comparison of Rational Numbers
1. To compare the two positive rational numbers we need to make their denominator same, then we can easily compare them.
Example
Compare 4/5 and 3/8 and tell which one is greater.
Solution
To make their denominator same, we need to take the LCM of the denominator of both the numbers.
LCM of 5 and 8 is 40.
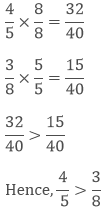
2. To compare two negative rational numbers, we compare them ignoring their negative signs and then reverse the order.
Example
Compare − (2/5) and – (3/7) and tell which one is greater.
Solution
To compare, we need to compare them as normal numbers.
LCM of 5 and 7 is 35.
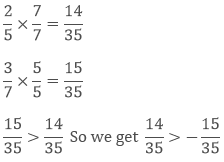
by reversing the order of the numbers.
![]()
3. If we have to compare one negative and one positive rational number then it is clear that the positive rational number will always be greater as the positive rational number is on the right to 0 and the negative rational numbers are on the left of 0.
Example
Compare 2/5 and – (2/5) and tell which one is greater.
Solution
It is simply that 2/5 > − (2/5)
Rational Numbers between Rational Numbers
To find the rational numbers between two rational numbers, we have to make their denominator same then we can find the rational numbers.
Example
Find the rational numbers between 3/5 and 3/7.
Solution
To find the rational numbers between 3/5 and 3/7, we have to make their denominator same.
LCM of 5 and 7 is 35.
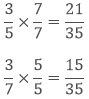
Hence the rational numbers between 3/5 and 3/7 are
![]()
These are not the only rational numbers between 3/5 and 3/7.
If we find the equivalent rational numbers of both 3/5 and 3/7 then we can find more rational numbers between them.
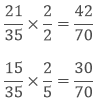
Hence we can find more rational numbers between 3/5 and 3/7.
Note: There are “n” numbers of rational numbers between any two rational numbers.
Operations on Rational Numbers
1. Addition
a. Addition of two rational numbers with the same denominator
(i) We can add it using a number line.
Example:
Add 1/5 and 2/5
Solution:
On the number line we have to move right from 0 to 1/5 units and then move 2/5 units more to the right.
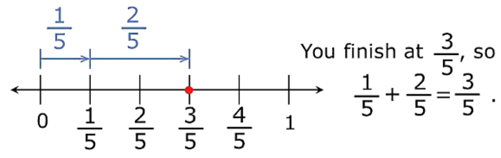
(ii) If we have to add two rational numbers whose denominators are same then we simply add their numerators and the denominator remains the same.
Example
Add 3/11 and 7/11.
Solution
As the denominator is the same, we can simply add their numerator.
![]()
b. Addition of two Rational Numbers with different denominator
If we have to add two rational numbers with different denominators then we have to take the LCM of denominators and find their equivalent rational numbers with the LCM as the denominator, and then add them.
Example
Add 2/5 and 3/7.
Solution
To add the two rational numbers, first, we need to take the LCM of denominators the find the equivalent rational numbers.
LCM of 5 and 7 is 35.
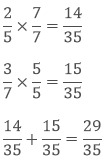
c. Additive Inverse
Like integers, the additive inverse of rational numbers is also the same.
a + (−a) = 0
This shows that the additive inverse of 3/7 is − (3/7)
This shows that
![]()
2. Subtraction
If we have to subtract two rational numbers then we have to add the additive inverse of the rational number that is being subtracted to the other rational number.
a − b = a + (−b)
Example
Subtract 4/21 from 8/21.
Solution
(i) In the first method, we will simply subtract the numerator and the denominator remains the same.
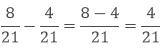
(ii) In the second method, we will add the additive inverse of the second number to the first number.
![]()
3. Multiplication
a. Multiplication of a Rational Number with a Positive Integer.
To multiply a rational number with a positive integer we simply multiply the integer with the numerator and the denominator remains the same.
Example
![]()
b. Multiply of a Rational Number with a Negative Integer
To multiply a rational number with a negative integer we simply multiply the integer with the numerator and the denominator remains the same and the resultant rational number will be a negative rational number.
Example
![]()
c. Multiply of a Rational Number with another Rational Number
To multiply a rational number with another rational number we have to multiply the numerator of two rational numbers and multiply the denominator of the two rational numbers.
![]()
Example
Multiply 3/7 and 5/11.
Solution
![]()
4. Division
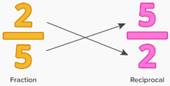
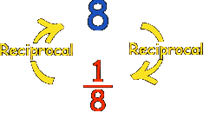
a. Reciprocal
Reciprocal is the multiplier of the given rational number which gives the product of 1.
Reciprocal of a/b is b/a
Product of Reciprocal
If we multiply the reciprocal of the rational number with that rational number then the product will always be 1.
Example
![]()
b. Division of a Rational Number with another Rational Number
To divide a rational number with another rational number we have to multiply the reciprocal of the rational number with the other rational number.
Example
![]() .
.
Solution
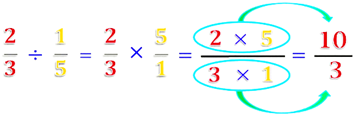
Online Tuitions and Self-Study Courses for Grade 6 to 12 & JEE / NEET
