Class 12 Chemistry
Magical Series Assignment
Organic Reasoning – Set 1
Write the reasons for the following …
Q.1. 3-Bromocyclohexene is more reactive than 4-bromocyclohexene towards hydrolysis with aqueous NaOH.
Q.2. Vinyl chloride is unreactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Q.3. p-Methoxybenzyl bromide is more reactive than p-nitrobenzyl bromide with ethanol to form ether.
Q.4. Although chlorine is highly electronegative, it undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution in o- and p- position.
Q.5. Carbon tetrachloride does not give precipitate with AgNO3 solution, while SiCl4 does so.
Q.6. Chlorobenzene (a haloarene) is extremely less reactive towards a nucleophilic substitution reaction than chloroethane (a haloalkane).
Q.7. Chloroform is stored in closed dark brown bottles, completely filled so that air is kept out.
Q.8. C – X Bond length in halobenzene is smaller than the C – X bond length in CH3 – X.
Q.9.
![]() reacts faster then
reacts faster then ![]() .
.
Q.10. Order of reactivity of haloalkanes is RI > RBr > RCl.
Q.11. Neopentyl chloride, (CH3)3CCH2Cl does not follow SN2 mechanism.
Q.12. Grignard reagents are prepared strictly under anhydrous conditions.
Q.13. Haloalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution whereas haloarenes undergo electrophilic substitution.
Q.14. Alkyl halides are polar yet they are immiscible with water.
Q.15. Haloalkanes easily dissolve in organic solvents.
Q.16. Chlorobenzene has lower dipole moment than cyclohexyl chloride.
Q.17. Reaction of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to alcohols while with alcoholic KOH, alkenes are major products.
Q.18. Alkyl halides react with KCN to form mainly alkyl cyanides (RCN) with some alkyl isocyanides (RNC), while with AgCN they form exclusively isocyanides.
Q.19. Methyl chloride reacts with silver nitrile to form mainly nitromethane, while with potassium nitrite it forms methyl nitrite-along with some nitromethane.
Q.20. Alkyl halides (R–X) are more reactive than aryl halides (Ar–X) towards nucleophilic substitution.
Q.21. Phosphoric acid (but not sulphuric acid) is used for preparing alkyl iodides from alcohols and potassium iodide.
CH3CH2OH + KI 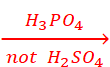 CH3CH2I + KOH
CH3CH2I + KOH
Q.22. Methylene chloride, CH2Cl2, having two chlorine has more dipole moment than chloroform (CHCl3) and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) having three and four chlorine respectively.
Q.23. p-Dichlorobenzene has higher melting point and lower solubility than the o- and m- isomers.
Q.24. Nucleophilic substitution of primary alkyl chlorides with sodium acetate is catalysed by sodium iodide.
Q.25. neo-Pentyl bromide, Me3CCH2Br, a 1° alkyl bromide reacts with aqueous NaOH to form 3° alcohol, (CH3)2C(OH)CH2CH3.
Online Tuitions & Self-Study Courses for Grade 6 to 12 & JEE / NEET
