Chapter 18 – Pollution of Air and Water
Very Important Questions Answers
Q.1. What are the different ways in which water gets contaminated?
Ans: Water gets contaminated by the following ways:
(i) Sewage wastes: Waste materials from toilets, laundry, kitchen sources are responsible for contaminating water.
(ii) Industrial wastes: The release of harmful chemical wastes from industries gets into the water bodies, thereby polluting them.
(iii) Agrochemicals: These chemicals get carried away to the water bodies from agricultural fields due to rains and floods which lead to water pollution.
Q.2. At an individual level, how can you help to reduce air pollution?
Ans: We can reduce air pollution by adopting the following steps:
(i) By saying no to crackers.
(ii) By using CNG and unleaded petrol.
(iii) By generating awareness about air pollution among friends and neighbours.
(iv) By using solar energy, hydropower instead of fossil fuels.
(v) By planting trees to reduce the level of carbon dioxide and air pollution.
(vi) Converting leaves into compost instead of burning them.
Q.3. Clear, transparent water is always fit for drinking. Comment.
Ans: Clear, transparent water is not always fit for drinking as it may have many disease carrying microbes and dissolved impurities that are not visible to unaided eyes. So, transparent water also needs to be purified by various processes.
Q.4. You are a member of the municipal body of your town. Make a list of measures that would help your town to ensure the supply of clean water to all its residents.
Ans: To ensure the supply of clean water to all residents, the following steps must be taken:
(i) The area around water pipes must be clean.
(ii) Chemical methods such as chlorination must be used for purifying water.
(iii) The main water source must be built in clean surroundings and should be maintained properly.
Q.5. Explain the differences between pure air and polluted air.
Ans: Differences between pure air and polluted air are as follows:
|
Pure air |
Polluted air |
|
The air which does not have any pollutant is called pure air. |
The air which has many pollutants that can cause various diseases is called polluted air |
|
It is free from germs and harmful gases. |
It contains harmful gases and unwanted substances. |
|
All the gases are in correct ratio. |
Harmful gases are in a higher ratio. |
|
It has no smell. |
It has filthy smell. |
|
No SPMs in the air. |
High level of SPMs in the air. |
|
It is not harmful for living begins. |
It is harmful for living beings. |
Q.6. Explain circumstances leading to acid rain. How does acid rain affect us?
Ans: Air pollutants like sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide react, with the water vapour present in the atmosphere and forms sulphuric acid and nitric acid respectively. These acids drop down with rain as acid rain.
Acid rain affects us in the following ways:
(i) It corrodes the marble of the monuments such as Taj Mahal.
(ii) It damages our crops and also makes them poisonous.
(iii) It causes damage to aquatic life due to decreased O2.
(iv) The low pH of acid rain water changes the rate of metabolism of organisms.
Q.7. Which of the following is not a greenhouse gas?
(a) Carbon dioxide (b) Sulphur dioxide (c) Methane (d) Nitrogen
Ans: (d) Nitrogen is not a greenhouse gas. It is naturally found in the air and is a major constituent of it.
Q.8. Describe the 'greenhouse effect' in your own words.
Ans: Greenhouse effect is caused by greenhouse gases, e.g. CO2, CH4 and water vapour. When solar radiations reach the earth, some of these radiations are absorbed by the earth and then released back to the atmosphere.
Greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere trap these radiations and do not allow heat to escape out.
This keeps our planet warm and thus helps in human survival. However, an indiscriminate increase in the amount of greenhouse gases can lead to excessive increase in the earth's temperature leading to global warming.
Q.9. Prepare a brief speech on global warming. You have to deliver the speech in your class.
Ans: Global warming is an increase in the average temperature of the earth's surface. It occurs as a result of increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The greenhouse gases such as CO2, CH4, etc are increasing due to human activities including vehicular emissions, burning of fossil fuels, etc.
Global warming has become a major concern for governments worldwide. This is because even as little as 0.5°C rise in temperature can have serious implications.
Q.10. Describe the threat to the beauty of the Taj Mahal.
Ans: India's most famous tourist attraction 'Taj Mahal' is located at Agra. It has become a matter of concern in recent years due to increasing air pollution. Taj Mahal is made up of white marble. Experts have warned that air pollution is discolouring its white marble. The industries located around Agra produce pollutants like sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide. These gases react with water vapours to form sulphuric acid and nitric acid respectively. These acids come down along with rain as acid rain and corrodes the white marble of Taj Mahal. This phenomenon is also called as ‘marble cancer’.
Q.11. Why does the increased level of nutrients in the water affect the survival of aquatic organisms?
Ans: The increased level of nutrients in the water increases the growth of algae. Once these algae die, they serve as food for decomposers like bacteria. A lot of oxygen is utilised in this process, consequently leading to a decrease in the level of Dissolved Oxygen (DO) in the waterbody. This, in turn causes fishes and other aquatic organisms to die.
Q.12. We need to filter water before drinking. Give reason.
Ans: Water contains many disease carrying microbes and dissolved impurities that are not visible to unaided eyes. So, we need to filter water before drinking.
Q.13. A fuel can be used in vehicles in place of petrol and diesel. Name it.
Ans: CNG can be used in place of petrol and diesel in vehicles.
Q.14. Groundwater also gets polluted by sewage. How?
Ans: Untreated or inadequately treated sewage is major source of groundwater pollution. Sewage contains food wastes, detergents, microorganisms, etc. which seeps into the ground to pollute groundwater.
Q.15. Name two gases which are mainly responsible for acid rain.
Ans: Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide are the two gases mainly responsible for acid rain.
Q.16. In which category of pollutants are Microorganisms, such as bacteria, placed?
Ans: Microorganisms (pathogens) such as viruses are placed in biological water pollutants category.
Q.17. Run-off water from a garden is not considered a point source of pollution. Give reason.
Ans: Run-off from a garden is not considered a point source of pollution because this water does not have a specific location for its discharge pollutants.
Q.18. The use of excessive fertilisers and pesticides leads to the deficiency of an important substance in water. Name the substance.
Ans: The substance is oxygen.
Q.19. A part of radiation is absorbed by CO2. Write the name of this part.
Ans: Infrared radiation is absorbed by CO2.
Q.20. What are alternative fuels?
Ans: Alternative fuels can be used in place of fossil fuels to reduce pollution, e.g. solar energy.
Q.21. Combustion of fossil fuels generates a lot of air pollution. Can you suggest any two alternative, sources of energy which do not cause any pollution?
Ans: Combustion of fossil fuels generates a lot of air pollution. Solar energy and wind energy are two alternative sources of energy which do not cause any pollution.
Q.22. The quality of air at various locations is monitored regularly by government and other agencies. In what way can you use these data?
Ans: The quality of air at various locations is monitored regularly by government and other agencies. These data can be used to generate awareness about air pollution among people.
Q.23. For what purpose, bacteria present in faeces is used?
Ans: The bacteria present in the faeces are used as indicators of the quality of water.
Q.24. Name the chemicals which are used in refrigerators and air conditioner and damage ozone layer when released in air.
Ans: Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are the chemical compounds which are used in refrigerators, air conditioners and aerosol sprays, and damage ozone layer when released in air.
Q.25. An alternative fuel for vehicl.es is CNG. Write its full form.
Ans: CNG is Compressed Natural Gas.
Q.26. State whether acid rain affects the soil and plants.
Ans: Acid rain affects both the soil and plants. It decreases the pH value of soil, thus making the soil acidic which. is harmful for plants.
Q.27. A gas X is present in the stratosphere that prevents Y radiations of the sun from reaching the earth. This gas is getting depleted by CFCs. Identify X and Y.
Ans: X is ozone, Y is Ultraviolet (UV) rays.
Q.28. Mention two sources of air pollution that are not due to humans.
Ans: Volcanoes and dust-storms are natural sources of air pollution.
Q.29. Is smog an air pollutant?
Ans: Smog is a deadly air pollutant formed by the combination of smoke and fog.
Q.30. A gas is known to reduce the oxygen carrying capacity of blood. Mention its name.
Ans: Carbon monoxide (CO) reduces the oxygen carrying capacity of blood.
Q.31. Respiratory problems are caused by which type of pollution?
Ans: Air pollution causes respiratory problems.
Q.32. Air is a mixture of gases. Give the percentage of nitrogen and oxygen in clear air.
Ans: Clear air contains about 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen.
Q.33. A phenomenon that occurs naturally benefits life on the earth. The excess of it causes global warming. Name the phenomenon.
Ans: The phenomenon is greenhouse effect.
Q.34. A gas in majorly responsible for greenhouse effect. Write the name of this gas.
Ans: Carbon dioxide (CO2) is majorly responsible for greenhouse effect.
Q.35. Name any two water pollutants which are toxic for both plants and animals.
Ans: Lead and arsenic are two water pollutants which are toxic for both plants and animals.
Q.36. Why hot water released by powerplants and industries is considered a pollutant.
Ans: Hot water released by powerplants and industries is considered a pollutant because it raises the temperature of the water body. The high temperature of water reduces its oxygen content. This adversely affects the animals and plants living in it.
Q.37. A poisonous gas P is produced by incomplete combustion of fuels such as coal. This gas interferes with Q of blood and reduces its capacity to carry gas R. Instead, it combines itself with Q forming S. What are P, Q, R, S?
Ans: P is carbon monoxide, Q is haemoglobin R is oxygen and S is carboxyhaemoglobin.
Q.38. Give the sources and effects of following air pollutants.
(a) Carbon Monoxide (b) Sulphur oxides and Nitrogen oxides
(c) CFCs (d) SPMs.
Ans: Sources and effects of air pollutants are given below:
(a) Carbon Monoxide (CO)
It is produced in high levels by incomplete combustion of fuels such as petrol, diesel, coal and kerosene in homes, vehicles and thermal power plants. It is a poisonous gas that interferes with the oxygen carrying capacity of the blood. Haemoglobin of the blood combines with oxygen of air to form oxyhaemoglobin, that gives up O2 to cells. CO displaces O2 from oxyhaemoglobin to form carboxyhaemoglobin, that cuts off O2 supply and may even lead to death.
(b) Sulphur and Nitrogen Oxides
These are produced by combustion of fuels like coal in power plants petrol and diesel in vehicles and volcanic eruptions, etc. These oxides attack breathing system and lead to lung congestion and can cause respiratory problems, including permanent lung damage.
They also produce acid rain and contributes to formation of smog. Petroleum refineries are a major source of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide.
(c) Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
These are industrially useful gases but behave as air pollutants because of their damaging effect on ozone layer in the stratosphere. These are used in refrigerators, air conditioners and aerosol sprays. CFCs released into the air go up and react with the ozone destroying it gradually.
Ozone layer prevents the harmful ultraviolet radiations of the sun from reaching the earth. The destruction of ozone layer by CFCs will allow the extremely harmful ultraviolet radiations of the sun to reach the earth. This causes skin cancer, cataract and destruction of plants including crops. In fact, the destruction of ozone layer over Antarctica (South pole of the earth) has led to the thinning of this layer. It is called 'ozone hole'. The good news is that less harmful chemicals are now being used in place of CFCs such as hydrochlorofluorocarbons, hydrocarbons, etc.
(d) Suspended Particulate Matter (SPM)
These are mainly released from automobiles which burn diesel and petrol, or during industrial processes like steel making, mining and power plants. These reduce visibility and when inhaled, these particles irritate and damage lungs. They cause frequent attacks of asthma and bronchitis.
Q.39. There is a decline in population of fish-eating birds, when the water body is near an agricultural field. Is it true? Give reason for your answer.
Ans: Yes, there will be a decline in population of fish-eating birds. This is because of pesticides like DOT which are used in agricultural. fields to protect the crop.
These pesticides cannot be metabolised, i.e. if it gets into the body of fishes through water, it won’t be excreted out. It will pass on to the other animals consuming the fish (birds in this case). The birds thus get poisoned on eating the fishes, leading to their death and decline in their population.
Q.40. A lot of dry leaves are collected in a school garden and are burnt every day. Do you think that it is right to do so? If not, what should be done to dispose off the dry leaves?
Ans: No, it is not right to burn dry leaves as it causes air pollution. The right way to dispose off the dry leaves is to convert them into compost.
Q.41. Ozone depletion is one of the major concerns of governments around the world. What depletes the ozone layer in the atmosphere? What are the harmful effects of depletion of ozone layer on us?
Ans: Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) released into the air, go up and react with the ozone, destroying it gradually. The destruction of ozone layer will allow the extremely harmful ultraviolet radiations of the sun to reach the earth. This causes skin cancer, cataract and destruction of plants including crops.
Q.42. Comment on the Ganga Action Plan. What does it aim at?
Ans: Ganga Action Plan was launched in 1986 to save the river Ganga from getting polluted. It aims at improving the water quality by interception, diversion and treatment of water entering into river.
Q.43. Study the diagram which shows a factory discharging harmful chemical waste into a nearby river.
Which part of the river is the most polluted?
Which part of the river will you be able to find the most fish still surviving?
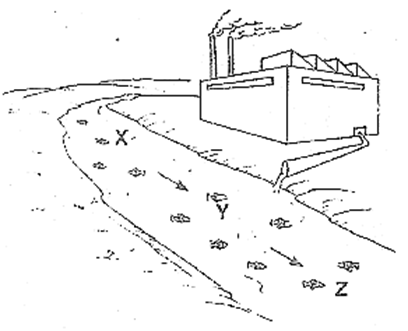
Ans: Z is the most polluted part of the river.
Most fishes are still surviving in part X. The arrows show the direction of the river flow as it moves downstream. The harmful chemical waste that is being discharged by the factory moves downwards to parts Y and Z of the river. It cannot move upstream as it is against the flow of river. Thus, X is the least affected part by the harmful chemical wastes.
Q.44. At many places the waste water containing human excreta from homes is carried in big underground pipes and dumped into a river as such which pollutes the river water.
(a) A common name is given to such waste water. What is it?
(b) Name five types of harmful organisms contained in it.
(c) Mention any five human diseases caused by drinking river water contaminated with such wastewater.
Ans:
(a) Sewage is the common name of such waste water.
(b) Harmful organisms contained in it are bacteria, Protozoa, fungi, viruses and parasites.
(c) Human diseases caused are cholera, typhoid, diarrhoea; dysentery and jaundice.
Q.45. Name any two sources which cause air pollution due to SPM.
Ans: Two sources which cause air pollution due to SPM are as follows:
(i) Automobiles which burn diesel and petrol, produce SPM that remain suspended in air and reduce visibility. When inhaled, they cause diseases.
(ii) Industrial activities like manufacturing of steel and mining give out SPM which also pollute the atmosphere.
Q.46. Air at a place is said to be polluted. What does it mean? Give the composition of air around us.
Ans: This means that air is contaminated by the addition of unwanted and harmful substances which are injurious to living organisms, property or interferes with normal environmental processes. This is called air pollution.
The air around us is a mixture of various gases. It is composed of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and remaining 1% by CO2, Ar, CH4, O3 and water vapour.
Q.47. Global warming causes various serious effects to life on earth. Mention some of these effects.
Ans: Effects of Global Warming:
(i) The high temperature will result in melting of polar ice caps which will lead to rise in sea level and many coastal areas will be submerged (e.g. the Gangotri glacier in Himalayas has started melting).
(ii) The high levels of temperature lead to increased weed growth, eruption of diseases and pests. Thus, the crop productivity will decrease.
(iii) It could result in wide ranging effects on rainfall patterns, agriculture, forests, plants and animals.
Q.48. Industries cause water pollution, describe its effect.
Ans: Industries oil refineries, paper factories produce toxic chemicals that are often discharged into rivers or streams, thereby polluting the water, e.g. The chemicals include pollutants such as arsenic, lead, fluorides, mercury, etc which lead to toxicity in plants and animals.
Effects The water polluted with toxic industrial wastes can kill aquatic animals. On reaching human body, it can damage nervous system and cause disease such as cancer.
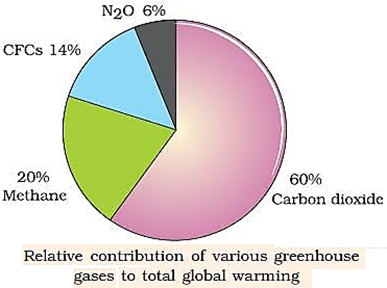
Q.49. Greenhouse effect is due to certain gases known as greenhouse gases. Name the greenhouse gases. How much is contributed by each of them towards global warming?
Ans: Carbondioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4), Chlorofluorocarbon (CFC), Nitrous oxide (N2O) are known as Greenhouse gases. Percentage contribution of these gases is given below.
Q.50. Explain the cause of algal bloom in a water body. How does it affect the water of the waterbody?
Ans: Algal bloom is caused by the enrichment of nutrients in the water body. The nutrients from the fertilisers, etc cause rapid growth of algae. It affects in following ways:
(i) Deteriorate the water quality.
(ii) Lead to death of aquatic organisms.
Q.51. By the end of 2002, public transport of Delhi switched over to a new fuel. Name the fuel. Why is this fuel considered better?
Ans: New fuel adopted was CNG (Compressed Natural Gas). It is a better fuel because
(i) it is cheaper than petrol.
(ii) it burns very efficiently.
(iii) it cannot be adulterated.
Q.52. The level of air pollution is higher at a busy traffic intersection. Why?
Ans: A large number of automobiles stop for a short period at red light throughout the day and release a large quantity of gases (due to burning of petrol and diesel) which leads to air pollution. Motor vehicles are the major cause of air pollution in big cities.
Q.53. Classification of water pollutants is important for its prevention. What are the various types of water pollutants?
Ans: Water pollutants can be classified into following three categories:
(i) Physical water pollutants These include heat and oil spills. High temperature of water reduces its oxygen content.
(ii) Biological water pollutants These include pathogens e.g. viruses, Protozoa, fungi, etc.
(iii) Chemical water pollutants include organic wastes, e.g. sewage detergents, fertilisers, etc.
Q.54. In metro cities, level of air pollution is higher. Mention the major causes responsible for this increase.
Ans: Major causes of air pollution are
(i) Emissions from automobile exhaust.
(ii) Effluent from thermal power plants.
(iii) Smoke from forest fires, volcanic eruptions, etc.
(iv) CFCs used in refrigerators, ACs, etc.
(v) Industrial processes such as steel making, mining, etc.
Q.55. Rohan was keen on knowing about the advertisements promoting RO units for purification of water for domestic use. He asked his teacher whether it is required or not. The teacher explained him happily.
(a) Give the meaning of RO.
(b) Will you suggest people to use RO? Why?
Ans: (a) RO is Reverse Osmosis. Water is passed through a semipermeable membrane that has fine pores. It allows water to pass through but not the impurities.
(b) Yes, I would suggest people to use RO. It is advantageous as it removes solid impurities as well as germs.
Q.56. Water that is suitable for drinking, is assigned a particular name. What is it? Explain various methods that can be used to make water drinkable.
Ans: The water which is suitable for drinking is called potable water.
Methods that can be used are:
(i) Boiling Many households use boiling as a method for obtaining safe drinking water. Boiling kills the germs present in the water. Boiling water for 15-20 min kills all germs.
(ii) Filtration It is a physical method of removing impurities. A popular household filter is a candle type filter.
(iii) Ultraviolet light It is used in several water purifiers available in the market today. It kills all the germs.
(iv) Reverse Osmosis (RO) Water is passed through a special membrane called a semipermeable membrane. It has very fine pores through which water can pass through but not the impurities. RO water filters are commonly available in the market, they remove solid impurities as well as germs.
(v) Chlorination It is a commonly used chemical method for purifying water. It is done by adding chlorine tablets or bleaching powder to the water. We should not use more chlorine tablets than specified.
Q.57. What do you understand by the term greenhouse effect?
Ans: The greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon where the atmosphere traps part of the sun's energy for heating the earth's surface. Without the natural greenhouse effect, the average temperature of the earth's surface would be below freezing point of water. Thus, natural greenhouse effect makes life possible.
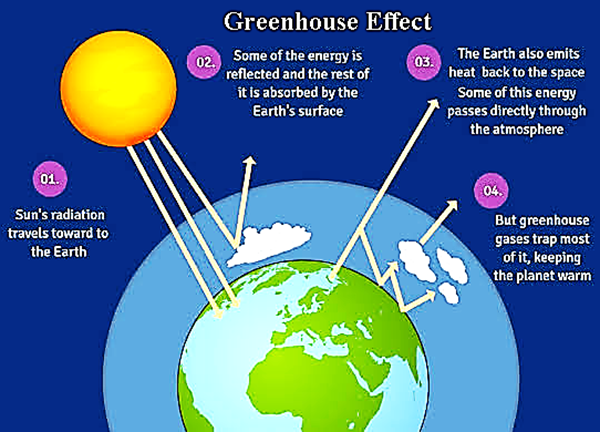
Clouds and gases reflect about one-fourth of the incoming solar radiation and absorb some of it. But almost half of incoming solar radiation falls on earth's surface heating it, while a small proportion is reflected back.
Earth's surface re-emits heat in the form of infrared radiation but part of this does not escape into space (similar to a greenhouse, where sun's heat is allowed to get in but is not allowed to go out) and atmospheric gases (e.g. carbon dioxide, methane, etc.) absorb a major fraction of it. These gases radiate heat energy and a major part of which again comes to earth's surface, thus heating it up once again. This cycle is repeated again and again. The gases like carbon dioxide and methane, etc. are commonly known as greenhouse gases because they are responsible for the greenhouse effect.
Q.58. The need of the hour is to take appropriate measures to control water pollution. List some of these preventive measures.
Ans: Water pollution can be prevented or minimised by adopting measures as suggested below:
(i) Sewage should be treated properly before discharging it into nearby rivers.
(ii) Laws for industrial units should be strictly implemented. (Industries are supposed to treat the waste produced before discharging it into water, but queue often the rules are not followed).
(iii) Water treatment plants should be installed in all industrial areas.
(iv) The use of excessive fertilisers and pesticides should be avoided.
(v) We should consciously make efforts at individual level to conserve water. Some of the steps that can be taken are
(a) Adopt the mantra of reduce, reuse and recycle (3R).
(b) Turn off the tap immediately after use. Get the leaking taps repaired. (A tap that drips once every second wastes a few thousand litres of water every year).
(c) Use water, used for washing vegetables may be used to water plants in the garden.
(d) Create awareness among people.
Q.59. Why is it advised that industries should switch over to cleaner fuels such as CNG and LPG in the Taj Mahal zone in Agra?
Ans: The air pollution is turning the marble of Taj Mahal yellow and also corroding it slowly.
A survey found that it is due to the risen pollution levels in and around Agra, as a result of growth in industry, traffic and population.
The industries like rubber processing, automobile, chemicals and especially the Mathura oil refinery, have been responsible for producing pollutants like SO2 and NO2 that lead to acid rain. Acid rain corrodes the marble of the monument. This phenomenon is also called marble cancer.
Suspended particulate matter (SPM) such as the soot particles emitted by Mathura oil refinery, has contributed towards the yellowing of the marble.
Considering the aforementioned factors, in order to save the Taj Mahal from marble cancer and corrosion, it is advised that industries should switch over to cleaner fuels such as CNG and LPG in the Taj Mahal zone in Agra
Q.60. Read the paragraph and answer the questions following it. Water is essential for life. Without Water there would be no life. We usually take water as granted for its purity, but we must ensure the quality of water. Pollution of water originates from human activities. Through different paths, pollution reaches to groundwater. Easily identified source or place of pollution is called as point source, e.g. municipal and industrial discharge pipes, where pollutants enter the water source. Non-point sources of pollution are those where a source of pollution cannot be easily identified, e.g. agricultural run-off, acid rain, etc.
(a) How do you classify the various sources of water pollution?
(b) What are the point sources of water pollution?
(c) Name any two non-point sources of water pollution?
Ans:
(a) Various sources of water pollution are classified as point sources and non-point sources.
(b) The sources or places of pollution which are easily identifiable are point sources of water pollution. e.g., factories, power plants, etc.
(c) Agricultural run-off and acid rain are non-point sources of water pollution.
Q.61. An Indian holy river is among the ten most endangered rivers list of WWF. Which is it? How is the water of this river polluted?
Ans: The Ganga is the Indian holy river that is amongst the ten most endangered rivers list of WWF. The water has been highly polluted because the towns and cities through which the river flows, throw huge quantities of garbage, untreated sewage, dead bodies and many other harmful things, directly into the river. In fact, the river is dead at many places where the pollution levels are extremely high.
Q.62. What do CFCs stand for? Name some devices where CFCs are used. Why CFCs are considered as pollutants?
Ans: CFCs stand for chlorofluorocarbons.
CFCs are used in refrigerators, air conditioners and aerosol sprays.
CFCs are considered as pollutants because these are depleting the useful ozone layer of the upper atmosphere.
CFCs released into the air, go up and ultimately reach high into the atmosphere where the protective ozone layer exists. The chlorofluorocarbons react with ozone gas of ozone layer and destroy it gradually. This allows the harmful ultraviolet rays of the sun to reach the earth and cause damage.
Q.63. It is said, 'CO2 contributes to global warming.' Explain.
Ans: CO2 contributes to global warming because when the amount of CO2 gas in the atmosphere increases leading to excessive heating of the earth and its atmosphere.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is one of the components of air. If there is excess of CO2 in the air, it acts as a pollutant. Deforestation leads to an increase in the amount of CO2 in the air because the number of trees which consume CO2 is reduced. This contributes to accumulation of CO2 in the atmosphere. It greatly intensifies the natural greenhouse effect, causing global warming.
Q.64. Arjun while travelling with his father saw the same message displayed at every traffic signal. The message was 'stop the vehicle engine at the red lights to save the fuel'. He noticed his father turning the engine off at each signal. He was confused to see this and asked his father.
(a) It is recommended to stop the vehicle engine at the red-light signals. Give reason.
(b) Suggest the process associated when vehicle engine is ON.
(c) What values. are government trying to inculcate in people with the message?
(d) Will you support the message? Why?
Ans:
(a) It is recommended to stop the vehicle engine at the red-light signals to minimise the emissions of poisonous gases like CO, NO, etc from the automobile exhaust.
(b) With the vehicle engine ON, the incomplete combustion of fuel will take place with release of gases like CO.
(c) The government is trying to make people understand the need for reducing environment pollution and the small steps that they can take for environmental protection.
(d) Yes, I will support the message. It is for the common good.
Q.65. Explain the phenomenon of marble cancer. Mention the steps taken by the supreme court to save the Taj Mahal from air pollution.
Ans: The industries like rubber processing, automobile, chemical and refinery produce pollutants like sulphur and nitrogen dioxide that leads to acid rain. Acid rain corrodes the marble of the monument. This phenomenon is also called marble cancer.
To save the Taj Mahal from air pollution, the Supreme Court of India has ordered industries to switch to cleaner fuels like CNG (Compressed Natural Gas), LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) and unleaded petrol in the Taj zone.
Q.66. We should plant trees and nurture the ones already present in the neighbourhood. Why?
Ans: We should plant trees and nurture the ones already present in the neighbourhood. This is to
(i) Reduce air pollution: Plants clean the air. They also reduce dust particles in the air: This will lower down the "pollution level.
(ii) Minimise global warming: The greenhouse gas CO2 is responsible for global warming. Plants utilise CO2 for making food and give out 02. Therefore, planting more trees will reduce the CO2 in atmosphere and thus global warming will be in control.
Online Tuitions & Self-Study Courses for Grade 6 to 12 & JEE / NEET
