Class 8 Mathematics
Chapter 7 – Cube and Cube Roots
Chapter Notes
Cubes
Cube is a 3-dimensional figure with all equal sides. If one cube has all the equal sides of 1 cm then how many such cubes are needed to make a new cube of side 2 cm?
8 such cubes are needed, and what if we need to make a cube of side 3 cm with the cubes of side 1 cm? The numbers 1, 8, 27 ...etc can be shown below in the cube.
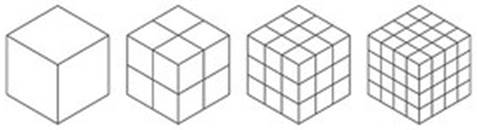
These are known as perfect cubes or cube numbers. This shows that we got the cube numbers by multiplying the number three times by itself.
Cubes of Some Natural Numbers
|
Number |
Cubes |
Numbers |
Cubes |
|
1 |
13 = 1 |
11 |
113 = 1331 |
|
2 |
23 = 8 |
12 |
123 = 1728 |
|
3 |
33 = 27 |
13 |
133 = 2197 |
|
4 |
43 = 64 |
14 |
143 = 2744 |
|
5 |
53 = 125 |
15 |
153 = 3375 |
|
6 |
63 = 216 |
16 |
163 = 4096 |
|
7 |
73 = 343 |
17 |
173 = 4913 |
|
8 |
83 = 512 |
18 |
183 = 5832 |
|
9 |
93 = 729 |
19 |
193 = 6859 |
|
10 |
103 = 1000 |
20 |
203 = 8000 |
This table shows that
· There are only 10 perfect cubes between 1-1000.
· The cube of an even number is also even.
· The cube of an odd number is also an odd number.
One’s digit of the Cubes
One’s digit of the Cubes of a number having a particular number at the end will always remain same. Let’s see in the following table:
|
Unit’s digit of number |
Last digit of its cube number |
Example |
|
1 |
1 |
113 = 1331, 213 = 9261, etc. |
|
2 |
8 |
23 = 8, 123 = 1728, 323 = 32768, etc. |
|
3 |
7 |
133 = 2197, 533 = 148877, etc. |
|
4 |
4 |
243 = 13824, 743 = 405224, etc. |
|
5 |
5 |
153 = 3375, 253 = 15625, etc. |
|
6 |
6 |
63 = 216, 263 = 17576,etc. |
|
7 |
3 |
173 = 4913, 373 = 50653,etc. |
|
8 |
2 |
83 = 512, 183 = 5832, etc. |
|
9 |
9 |
193 = 6859, 393 = 59319, etc. |
|
10 |
20 |
103 = 1000, 203 = 8000, etc. |
Some Interesting Patterns
1. Adding Consecutive Odd Numbers

This shows that if we add the consecutive odd numbers then we get the cube of the next number.
2. Cubes and their Prime Factors
Prime factorization of a number is done by finding the prime factors of the number and then pairing it in the group of three. If all the prime factors are in the pair of three then the number is a perfect cube.
Consider,
the number 216. By prime factorisation,
216 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 = 23 × 33
= 63
Hence, 216 is a perfect cube.
Consider,
the number 500. By prime factorisation,
500 = 2 × 2 × 5 × 5 × 5 = 22 × 53
In the above prime factorisation 2 appears twice (not
thrice).
Hence, 500 is not a perfect cube.
Example
Calculate the cube root of 13824 by using prime factorization method.
Solution
First of all write the prime factors of the given number then pair them in the group of three.
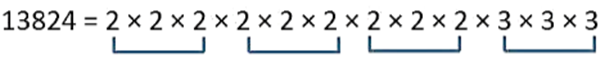
Since all the factors are in the pair of three the number 13824 is a perfect cube.
Smallest Multiple that is a Perfect Cube
As we have seen that the group of three prime factors makes a number perfect cube, so to make a number perfect cube we need to multiply it with the smallest multiple of that number.
Example
Check whether 1188 is a perfect cube or not. If not then which smallest natural number should be multiplied to 1188 to make it a perfect cube?
Solution
1188 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 11
This shows that the prime numbers 2 and 11 are not in the groups of three. So, 1188 is not a perfect cube
To make it a perfect cube we need to multiply it with 2 × 11 × 11 = 242, so, it will make the pair of 2, 3 and 11.
Hence the smallest natural number by which 1188 should be multiplied to make it a perfect cube is 242.
And the resulting perfect cube is 1188 × 242 = 287496 ( = 663).
Cube Roots
Symbol of
the Cube Root : 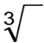
Finding cube root is the inverse operation of finding the cube.
If 33 =27 then cube root of 27 is 3.
We write it as ∛27 = 3
Note: In simple words, cube root is the length of the side of a cubic structure. If we represent a cube as x3, then x3 is the volume of the cube and x is the side of that cube.
Some of the cube roots are:
|
Statement |
Inference |
Statement |
Inference |
|
13 = 1 |
∛1 = 1 |
63 = 216 |
∛216 = ∛63 = 6 |
|
23 = 8 |
∛8 = ∛23 = 2 |
73 = 343 |
∛343 = ∛73 = 7 |
|
33 = 27 |
∛27 = ∛33 = 3 |
83 = 512 |
∛512 = ∛83 = 8 |
|
43 = 64 |
∛64 = ∛43 = 4 |
93 = 729 |
∛729 = ∛93 = 9 |
|
53 = 125 |
∛125 = ∛53 = 5 |
103 = 1000 |
∛1000 = ∛103 = 10 |
Method of finding a Cube Root
There are two methods of finding a cube root
1. Prime Factorization Method
Step 1: Write the prime factors of the given number.
Step 2: Make the pair of three if possible.
Step 3: Then replace them with a single digit.
Step 4: Multiply these single digits to find the cube root.
Example
Find the cube root of 15625 by the prime factorization method.

2. Estimation Method
If a cube number is given we can find out its cube root using the following steps:
- Take any cube number say 117649 and start making groups of
three starting from the rightmost digit of the number.
So, 117649 has two groups, and first group (649) and the second group (117). - The unit’s digit of the first group (649) will decide the unit digit of the cube root. Since the number 649 ends with 9, the cube roots unit’s digit is 9.
- Find the cube of numbers between which the second
group lies. The other group is 117. We know that 43 = 64 and
53 = 125.
64 < 117 < 125. Take the smaller number between 4 and 5 as the ten’s digit of the cube root. So, 49 is the cube root of 117649.
Differences of Squares of Triangular Numbers and Converse
Triangular numbers: It is a sequence of the numbers 1, 3, 6, 10, 15 etc. It is obtained by continued summation of the natural numbers. The dot pattern of a triangular number can be arranged as triangles. Sum of two consecutive triangular numbers gives us a square number. For example, 1+3=4=22 and 3+6=9=32.
The difference between the squares of two consecutive triangular numbers is a cube number. For example, 32−12=9−1=8=23 and 62−32=36−9=25=53.
Also, if the difference between the squares of two numbers is a cube number, then these numbers are consecutive triangular numbers.
Hardy-Ramanujan Number
The number which can be expressed as the sum of two cubes in different ways is said to be a Hardy – Ramanujan number.
1729 = 1728 + 1 = 123 + 13
1729 = 1000 + 729 = 103 + 93
As 1729 is the smallest such type of number so it is called the smallest Hardy-Ramanujan number. There is infinite such type of numbers. Like- 4104 (2, 16; 9, 15), 13832 (18, 20; 2, 24), etc.
Online Tuitions & Self-Study Courses for Grade 6 to 12 & JEE / NEET
