Forest is a natural renewable resource.
It is a habitat to enormous forms of wildlife species, such as monkeys, lions, bear, bison, jackal, deer, porcupine, elephant, snake, etc.
Structure of a Forest
The plants (trees, shrubs and herbs) make different layers in the forest which are described below:
1. Canopy
The uppermost layer of branches and leaves of tall trees which act like a roof over the forest ground is called canopy. It is the highest layer of vegetation in the forest. The branchy part of a tree above the stem is known as the crown of the tree.

2. Understorey
The different horizontal layers formed due to different types of crowns in the forest is called understorey.

The constituents of understorey:
(i) Top layer: It constitutes the giant and tall trees followed by shrubs and tall grasses.
(ii) Shrub layer: It has many shrubs and bushes of approximately 1-2 metres of height from the forest floor. It makes dense layer at some places of forest where enough sunlight is present.
(iii) Herb layer: Just below the shrub layer occurs the herb layer of plants. It is the lowest layer of vegetation (i.e., of Understorey) in the forest (having leafy plants). Most of the plants in herb layer have short lifespan.
3. Forest Floor
Plants found here are as small as mosses, liverworts, lichens. It has many kinds of insects, worms, toad stool, etc. Most of the forest floor is covered with dead and decaying plant matter, and animal waste.
Components of the Forest
The living organisms found in the forest are plants, animals, decomposers and scavengers. The non-living environment of the forest provides nutrients, water and carbon dioxide for the growth of the plants.
1. Plants
Green plants ate living organisms also called autotrophs as they produce food by photosynthesis (by absorbing nutrients water from soil, CO2 from air and sunlight as energy source). They provide food to all living organisms which live in the forest. They are called producers (of food).
2. Animals
Forests have many animals and they are called consumers (of food). The animals which eat only plants/their parts are called herbivores (herb eating) whereas flesh eating animals are called carnivores. All animals are called heterotrophs because they depend on other organisms for food.
3. Decomposers
Mostly these organisms are microorganisms like bacteria and fungi. They feed on dead plants and animals and thus are called saprotrophs.
These organisms are called decomposers as they breakdown dead parts of plants and dead bodies of animals into simple substances.
4. Scavengers
Those animals which eat dead animals are called scavengers, e.g., vultures, crows, jackals, hyena, some insects (ants, beetles, termites, wood lice, maggots, millipedes and earthworms), etc.
Scavengers are the cleaning agents of our environment.
Scavengers are not decomposers as they do not breakdown complex dead organic matter into simple ones.
Importance of Forests
1. Forests Provide Many Useful Products
The various things which are obtained from the forests are called forest products. Forests give us a large number of useful products. Some of the important products which we get from the forests are wood, honey, gum, sealing wax (or lac), catechu (kattha), fruits, oils, spices, natural rubber, cork, dyes, medicinal plants and fodder for cattle.

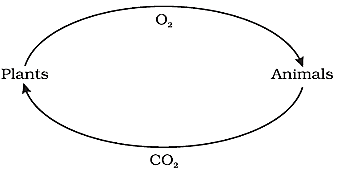
2. Forests Maintain Balance between Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Plants in the forest release oxygen during photosynthesis. This provides all animals including us with oxygen to breathe and helps to maintain the ratio of oxygen to carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. That is why, forests are called green lungs.
If amount of carbon dioxide increases in the atmosphere, it would result in increase in earth's temperature.
3. Forests Maintain Water Cycle
The forest trees absorb water from the soil through their roots and release water vapour into the air through transpiration. This water vapour helps in the formation of clouds and bring rain on the earth.
About half the rain which falls in forest areas comes from the transpiration of forest trees themselves. In this way, forests help in maintaining a perfect water cycle in nature and meet our freshwater requirements.
4. Forests Prevent Occurrence of Flood
The forest acts as a natural absorber of rainwater and allows it to seep. It helps to maintain the water table throughout the year.
Forests not only help in controlling floods but also help to maintain the flow of water in the streams so that we get a steady supply of water.
In absence of trees, rain would hit the ground directly and might flood the area around it.

Heavy rain may also damage the soil. Roots of trees normally bind the soil together, so that the soil is not washed away or eroded.
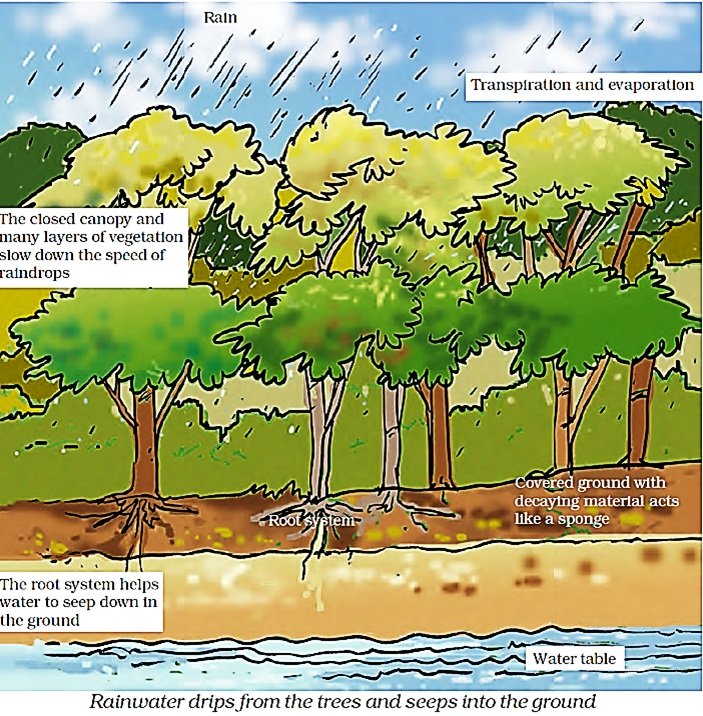
The different kinds of plants grow together in the forest making different levels of layers, which slow down the speed of rain drops falling on the ground.
5. Forests Provide Habitat for Wildlife
The different types of vegetation present in a forest provide food and shelter to animals, birds and insects which live in the forest. This makes a food chain.
Food chain
Food chain can be defined as a sequence of living organisms in which one organism feeds on another.
A typical chain in grassland is: grass → deer → lion
A typical food chain in a pond is: algae → small fish → large fish
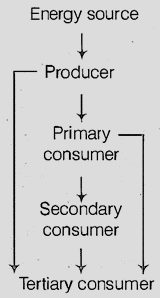
Flow of Energy in a Food Chain
The sun is the ultimate source of energy for everything on the planet. Green plants or producers are able to harness the energy of the sun to make food.
In a food chain, energy from plants (producers) is passed on from one organism to another. From the producers, the energy goes to primary consumers (herbivores) and is then passed on to secondary consumers (carnivores). Thus, producers are always at the beginning of the food chain.
Dynamic Living Entity
By harbouring greater variety of plants, the forest provides great opportunities of food and habitat for the herbivores.
Larger number of herbivores means increased availability of food for a variety of carnivores. The wide variety of animals helps the forest to regenerate and grow.
Decomposers help in maintaining the supply of nutrients to the growing plants in the forest. Therefore, the forest is a dynamic living entity. There is a continuous interaction between soil, water, air, plants and animals in a forest.
6. Forests can Regenerate on their Own
The dead parts of trees and plants, dead animals and animal wastes (like animal dung or droppings) keep on collecting on the forest floor.
Decomposers (fungi and bacteria) degrade them into simple organic substances which are usable by plants in the form of humus.
The humus makes the forest soil fertile by providing the nutrients.
The animals, birds of forests, wind and water disperse the seeds of trees and plants on the forest soil.
These seeds obtain nutrients from the soil and germinate to form seedlings and ultimately grow to form the forest vegetation.

Deforestation
Large number of forest trees are being cut down every day to meet the various demands of the increasing population. This is called deforestation.
Forest Conservation
Some ways to conserve forests are:
(i) Excessive cutting down of forest trees should not be allowed by the government to conserve forests.
(ii) More trees should be planted in the forest in place of cut down trees to conserve forests.
(iii) Paper products such as old newspapers, magazines, books, notebooks, etc., should be recycled to conserve forests.
Consequence of deforestation:
1. Loss of Habitat
One of the most dangerous and unsettling effects of deforestation is the loss of animal and plant species due to their loss of habitat. 70% of land animals and plant species live in forests.
2. Increase in Temperature
The trees of the rainforest that provide shelter for some species also provide the canopy that regulates the temperature. Deforestation results in a more drastic temperature variation from day to night, much like a desert, which could prove fatal for many inhabitants.
3. Increased Greenhouse Gases
Healthy forests absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, acting as valuable carbon sinks. Deforested areas lose that ability. Excess CO2 in atmosphere will lead to greater Greenhouse effect, which will further increase the earth’s temperature.
4. Less Water in the Atmosphere
The trees also help control the level of water in the atmosphere by helping to regulate the water cycle. In deforested areas, there is less water in the air to be returned to the soil. This then causes dryer soil and the inability to grow crops.

5. Soil Erosion and Flooding
Trees help the land to retain water and topsoil, which provides the rich nutrients to sustain additional forest life.
Without forests, the soil erodes and washes away. The barren land which is left behind in the wake of these unsustainable agricultural practices is then more susceptible to flooding, specifically in coastal regions.
6. Destruction of Homelands
As large amounts of forests are cleared away, allowing exposed earth to wither and die and the habitats of innumerable species to be destroyed, the indigenous communities who live there and depend on the forest to sustain their way of life are also under threat. The level of immediacy is exponentially greater for indigenous peoples.
Few Important Terms
Canopy
The uppermost layer of branches and leaves of tall trees which act like a roof over the forest ground is called canopy.
Crown
The branchy part of a tree above the stem is known as the crown of the tree.
Understorey
The different horizontal layers formed due to different types of crowns in the forest is called understorey.
Soil erosion
Soil erosion is the degradation of soil due to displacement of the upper layer of soil by water (rain), air (wind), deforestation, overgrazing, agrochemicals, etc.
Decomposers
Microorganisms like bacteria and fungi that feed on dead plants and animals and thus are also called saprotrophs.
Humus
Humus is the dark organic matter that forms in soil when dead plant and animal matter breaks down further, specifically through the action of anaerobic organisms. Humus has many nutrients that improve the health of soil, nitrogen being the most important. The ratio of carbon to nitrogen (C : N) of humus is 10 : 1.
Seed dispersal
Seed dispersal is the movement, spread or transport of seeds away from the parent plant. Plants have limited mobility and rely upon a variety of dispersal vectors to transport their propagules, including both abiotic vectors such as the wind and living (biotic) vectors like birds.
Deforestation
Deforestation is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land which is then converted to a non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, industries, or urban use.
Online Tuitions & Self-Study Courses for Grade 6 to 12 & JEE / NEET
