Symbols of Electric Components
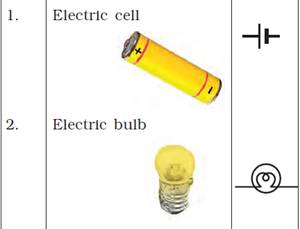
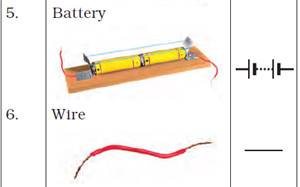
Connecting Multiple Cells
A combination of two or more cells is called a battery.
In most of the cases, we connect two or more cells together in series as shown in the figure below.
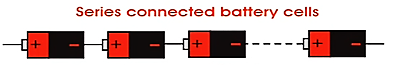
The positive terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the next cell.
This configuration provides higher voltage capacity. Resulting voltage is equal to the sum of voltages of each cell.
Sometimes the cells are placed side by side. This arrangement is commonly known as parallel connection.
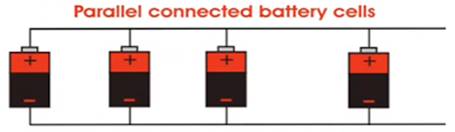
The positive terminals of all cells are connected together and the negative terminals of all the cells are connected together. Such a combination of two or more cells is also called a battery.
This configuration can provide higher current capacity. Maximum current can be equal to the sum of current capacity of each cell.
Cell Holder
The cell holder is used to arrange multiple cells in series or parallel configuration. Cell holders are normally used in TV/AC remotes, battery operated toys, digital blood pressure monitors, torch, etc.

Electric Charges
Electric charge of a material body or particle is the property due to which it produces and experiences electrical and magnetic effects.
Charges are of two types: positive charge and negative charge.
Protons are positively charged particles present in the nucleus of an atom.
Electrons are negatively charged particles which revolve around the nucleus.
Electric charges can neither be created nor be destroyed in an isolated system. This means electric charge is conserved.
The SI unit of charge is coulomb (C).
The rate of flow of electric charge through a conductor is called the electric current and it is denoted by I.
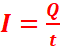
where, Q is the amount of charge
t is the time taken to flow Q amount of charge.
The SI unit of electric current is ampere which is denoted as A
Electric Circuit
A continuous conducting path (consisting of wires, bulb, switch, etc.) between the two terminals of a cell or battery along with an electric current flows, is known as electric circuit.
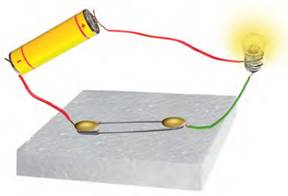
Positive terminal of the cell is connected to one end of the switch with a piece of copper wire.
Other end of the switch is connected to one end of bulb holder with another piece of copper wire.
The negative terminal of the cell is connected directly to the other end of the bulb holder with a wire.
This kind of setup is known as electric circuit.
Circuit Diagram
A circuit diagram tells us how the various components in an electric circuit have been connected by using the electrical symbols of the components.
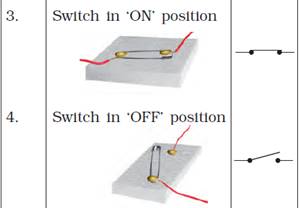
In an electric circuit when the switch is closed, then the switch is said to be in the ON position.
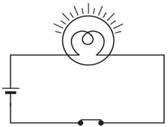
When the switch in a circuit is open, then the switch is said to be in the OFF position.
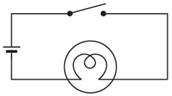
Sometimes the bulb does not glow even when the switch is in the ON position.
This condition can occur only if the bulb get fused, i.e. its filament breaks.
Heating Effect of Electric Current
Production of heat in an electric device due to flow of electric current is called heating effect of electric current.
We have seen an electric heater used for cooking, an electric bulb or room heater.
When these appliances are switched ON after connecting to the electric supply, then their elements become red hot and release the heat.
This happens due to heating effect of electric current.
Activity to understand the heating effect of electric current
Take about 10 cm long piece of nichrome wire and tie it between the two nails.
Make an electric circuit by connecting the two nails to the two terminals of a cell through a switch by using copper wire as shown in figure.
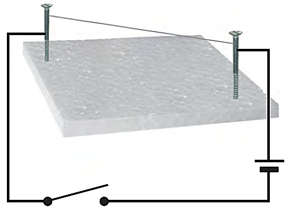
Now, by moving the switch to the ON position, switch ON the current in the circuit after some time (few seconds), touch the nichrome wire just for a moment.
We will find that the nichrome wire has become hot.
This is because the electric current passing through it has produced heat in it.
From this activity, we can conclude that when an electric current is passed through a high resistance wire like nichrome wire, the wire becomes hot and produces heat.
Resistance
The degree to which a material opposes the passage of current through itself is known as its resistance.
When an electric current passes through a high resistance wire, the electric energy gets converted into heat energy and this heat energy heats up the wire.
Element
Electrical heating devices consist of a coil of wire called an element.
There are some electric appliances such as immersion heaters, hotplates, irons, geysers, electric kettles, hair dryers, etc., which have elements inside them.

Electric iron element

Geyser element
When these appliances are switched ON after connecting to the electric supply, then their elements become red hot and release the heat.
Factors on Which the Heating Effect of Current Depends
Two factors on which the heating effect of current depends:
(i) Resistance of wire: Greater the resistance of a wire, greater will be the heat produced in it by a given current.
E.g. if we choose two wires, one of copper and other is nichrome of equal length and equal thickness and pass them the equal amount of current through them for the same duration, then we will notice that nichrome wire will become more hot in comparison to the copper wire.
It is due to the reason that the resistance of nichrome wire is more than that of the copper wire.
That is why the nichrome wire is used to make heating elements of electric heating appliances such as electric room heater, electric iron, etc.
Resistance of a wire depends on material of wire, length of wire and thickness of the wire.
(ii) Magnitude of current passed through a given wire: If the magnitude of current passed through a given wire is greater, then the heat produced in it will also be greater.
E.g. if a normal amount of current flows through the copper wires of household electric wiring, then the wires do not become much hot but if a large current flows in the same wiring accidently, then the wires become extremely hot and a fire may be started.
Applications of the Heating Effect of Current
(i) For the production of light, heating effect of electric current is utilised in the electric bulbs.

(ii) For the working of electrical heating appliances such as water heater, electric room heater, electric iron, etc., the heating effect of electric current is utilised.



(iii) The heating effect of electric current is utilised in a safety device called 'electric fuse'.

Fluorescent Tube-light, Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs)
An electric bulb is basically used for producing light but it also releases the heat which is not desirable because a major part of the electricity consumed by the filament of a bulb is converted into heat and results in the wastage of electricity.
This wastage can be decreased by using fluorescent tubelight or CFLs (as shown in figure) in place of the bulbs.


Before purchasing bulbs, tubes or CFL's we should look for the ISI mark (ISI- Bureau of Indian standard).
It is because the ISI mark ensures that the appliance is safe and wastage of energy is minimum.
Causes of Large Current Flow in Household Electric Wiring
An extremely large current can flow in the household electric wiring circuits under two circumstances overloading and short circuit.
Overloading
It is a situation when too many electrical appliances are connected to a single socket, they draw an extremely large amount of current from the household circuit.
The flow of large current due to overloading may heat the copper wires of household wiring to a very high temperature and fire may be started.
Short Circuit
Electric current is supplied by household through two insulated wires which run together and reach each and every electrical appliances.
One insulated wire is called live wire and the other insulated wire is called neutral wire and both these wires are necessary for the working of an electrical appliance (say an electric iron).
If in case the plastic insulation of the live wire and neutral wire gets torn due to wear and tear, then the two naked wires touch each other.
This touching of live wire and neutral wire directly is known as short circuit.
Due to which a large current flows through the household wiring and this large current may heat the wires to a dangerously high temperature and a fire may be started.
Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs)
These are increasingly being used these days in place of fuses.
MCB does not work on the heating effect of current as it works on the magnetic effect of current.

These switches automatically turn OFF when the current in a circuit exceeds the safe limit.
We turn them ON and the circuit is once again complete.
Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
If electric current passes through a wire, then the current carrying wire behaves like a magnet.
This phenomenon is known as magnetic effect of current.
It was discovered by a scientist Hans Christian Oersted who found that when electric current is passed in a wire, then the compass needle placed near it got deflected from its usual North-South position.
Activity to understand the magnetic effect of current
Take the cardboard tray from inside a discarded matchbox. Wrap an electric wire a few times around the cardboard tray. Place a small compass needle inside it.
At this time the needle of the compass aligns itself in North – South direction.
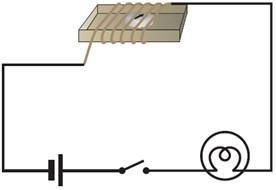
Now connect the free ends of this wire to an electric cell through a switch.
Now, we close the switch in such way that electric current passes through the wire.
We notice that the needle of the compass deflects from its original North-South position.
The deflection of compass needle shows that the current carrying wire coiled around it is behaving like a magnet and producing a magnetic field around it.
A straight wire carrying an electric current produces a magnetic effect.
The magnetic effect is increases if we use a long coil of wire instead of a straight wire.
The magnetic effect can be increased further, if the coil of wire is wound around an iron rod and then current is passed through it.
Electromagnets
It is a magnet made by using electric current.
An electromagnet works on the magnetic effect of current.
This magnet consists of a long coil of insulated copper wire wound around an iron rod or screw and when the two ends of the coil get connected to a cell, then a current passes through the coil and produces a magnetic effect.
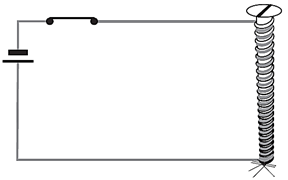
The magnetic effect magnetises the iron rod. In this way, the iron rod becomes an electromagnet.
The magnetism of an electromagnet remains as long as the current is flowing in its coil.
So, if we switch OFF the current in the coil, then all the magnetisms of the iron rod disappear and it will no longer behave like a magnet.
There are two factors through which an electromagnet can be made stronger, i.e.
(i) By increasing the amount of current used in the coil.
(ii) By increasing the number of turns forming the coil.
Uses of Electromagnets
(i) These magnets are used in electrical appliances such as electric bell, electric fan, electric motor.
(ii) These magnets have their utilisation in electric generators where very strong magnetic field is required.
(iii) For deflecting electron beam of the picture tube of TV, electromagnets are used.
(iv) For magnetic separation of iron ores from the earthly substances, electromagnets are used.
(v) For preparing strong permanent magnets, electromagnets are used.
Advantages of Electromagnets over Permanent Magnets
There are some of the advantages of the electromagnets over the permanent magnets which are stated as follows:
(i) The magnetism of an electromagnet can be switched ON or switched OFF as desired. While it is not possible with a permanent magnet.
(ii) By increasing the number of turns in the coil and by increasing the current passing through the coil an electromagnet can be made very strong. On the other hand, a permanent magnet cannot be made so strong.
Electric Bell
An electric bell works on the magnetic effect of electric current. It has an electromagnet in it.
It consists of a coil of wire wound on an iron piece.

The coil acts as an electromagnet.
An iron strip (armature) with a hammer at one end is kept close to the electromagnet.
There is a contact screw near the iron strip (armature). When the iron strip (armature) is in contact with the screw, the current flows through the coil which becomes an electromagnet.
It, then, pulls the iron strip.
In the process, the hammer at the end of the strip strikes the gong of the bell to produce a sound.
When the electromagnet pulls the iron strip (armature), it also breaks the circuit.
The current through the coil stops flowing.
The coil is no longer an electromagnet.
It no longer attracts the iron strip.
The iron strip comes back to its original position and touches the contact screw again.
This completes the circuit. The current flows in the coil and the hammer strikes the gong again.
This process of 'make and break' of the electric circuit continues as long as we keep the switch pressed (closed). The armature vibrates forwards and backwards rapidly each time making the clapper strike the gong and ringing the bell.
Online Tuitions and Self-Study Courses for Grade 6 to 12 & JEE / NEET
