Chapter 5 – Acids, Bases and Salts
Chapter Notes
Acids, bases, and salts are the groups of chemical substances which have different chemical properties.
Acids, bases, and salts are natural as well as man-made (artificial).
Edible substances and their tastes
|
Substance |
Taste (Sour/Bitter/Any other) |
Substance |
Taste (Sour/Bitter/Any other) |
|
Lemon juice |
Sour |
Sugar |
Sweet |
|
Orange juice |
Sour |
Common salt |
Salty |
|
Vinegar |
Sour |
Amla |
Sour |
|
Curd |
Sour |
Baking soda |
Bitter |
|
Tamarind (imli) |
Sour |
Grapes |
Sweet/Sour |
Acids and Bases
The word acid has been derived from a Latin word 'acidus' which means 'sour'. Thus, all sour substances essentially contain acids. Substances like lemon juice, orange juice, unripe mango, and curd taste sour. They taste sour because they contain substances called acids in them. The chemical nature of such substances is acidic. The acids in these substances are natural acids.
However, there are other substances like baking soda it does not taste sour.
It means that it has no acids in it. It is bitter in taste. And if we prepare a solution of baking soda in water and rub it between fingers, it feels soapy. Substance like these which are bitter in taste and feel soapy on touch are known as bases.
The chemical nature of such substances is said to be basic.
Acids and their sources
|
Name of acid |
Found in |
|
Acetic acid |
Vinegar |
|
Formic acid |
Ant's sting |
|
Citric acid |
Citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, etc. |
|
Lactic acid |
Curd |
|
Oxalic acid |
Spinach |
|
Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) |
Amla, citrus fruits |
|
Tartaric acid |
Tamarind, grapes, unripe mangoes, etc. |
All the acids mentioned in table occur in nature.
Bases and their sources
|
Name of base |
Found in |
|
Calcium hydroxide |
Lime water |
|
Ammonium hydroxide |
Window cleaner |
|
Sodium hydroxide/Potassium hydroxide |
Soap |
|
Magnesium hydroxide |
Milk of magnesia |
Natural Indicators Around Us
It is not safe to taste every substance to find out if it is acidic or basic. There are some special substances that have different colours in acidic and basic mediums. These substances are known as indicators. The indicators change their colour when added to a solution containing an acidic or a basic substance.
Some naturally occurring indicators are litmus, turmeric, China rose petals (gudhal) and red cabbage juice. These indicators show different colours in acidic and basic media. They are used to test whether a substance is acidic or basic in nature.
Litmus - A Natural Dye
A naturally occurring indicator, i.e., litmus is obtained from certain lichens (small plants) and used as a dilute solution.

Litmus have mauve (purple) colour in water. In an acidic solution, it turns red. When it is added to basic solution, it turns blue. Usually, it is available as red and blue litmus paper.

Activity 1: To show the effect of acidic and basic solutions on red and blue litmus paper.
Take the solution of lemon juice and water in a test tube or tumbler. Now put a drop of this solution on a strip of the red litmus paper with the help of a dropper. Note the colour change of litmus paper. Repeat the same exercise with blue litmus and again note the colour change. Observations of the activity with some test solutions are given below in tabular form.
|
Test solution |
Effect on red litmus paper |
Effect on blue litmus paper |
Inference |
|
Lemon juice |
No change |
Turns |
Acidic |
|
Tap water |
No change |
No change |
Neutral |
|
Detergent solution |
Turns blue |
No change |
Basic |
|
Aerated drink |
No change |
Turns red |
Acidic |
|
Soap solution |
Turns blue |
No change |
Basic |
|
Shampoo |
Turns blue |
No change |
Basic |
|
Common salt solution |
No change |
No change |
Neutral |
|
Sugar solution |
No change |
No change |
Neutral |
|
Vinegar |
No change |
Turns red |
Acidic |
|
Baking soda solution |
Turns blue |
No change |
Basic |
|
Milk of magnesia |
Turns blue |
No change |
Basic |
|
Washing soda |
Turns blue |
No change |
Basic |
|
Lime water |
Turns blue |
No change |
Basic |
When a red litmus paper strip dipped into basic solution, it turns blue.
When blue litmus paper dipped into acidic solution, it turns red in colour.
The solutions which do not change the colour of either red or blue litmus are known as neutral solutions.
Turmeric − A Natural Indicator
Turmeric is a bright yellow powder obtained from a plant. It is called 'Haldi' in Hindi. Turmeric contains a yellow dye. Turmeric turns red in basic solution. It is used as indicator in the form of turmeric paper.
Activity 2 − To prepare turmeric paper and effect of acidic or basic solution on it
Take a tablespoonful of turmeric powder, add a little water, and make a paste. Deposit the turmeric paste on a blotting paper (or filter paper) and dry it. The yellow paper thus obtained is turmeric paper. We can use thin strips of turmeric paper as indicator.
Now, if put a drop of soap solution on the strip of turmeric paper, then yellow colour of turmeric paper turns red. It shows that soap solution is basic in nature.
Test the solutions (with turmeric solution) listed in table and note the observation in tabular form.
Turmeric paper is yellow in acid solution, but bases turn the yellow turmeric paper to red.
|
Test solution |
Effect on turmeric solution |
Remarks |
|
Lemon juice |
Remains yellow |
Acidic |
|
Orange juice |
Remains yellow |
Acidic |
|
Vinegar |
Remains yellow |
Acidic |
|
Milk of magnesia |
Turns red |
Basic |
|
Baking soda |
Turns red |
Basic |
|
Lime water |
Turns red |
Basic |
|
Sugar |
No change |
Neutral |
|
Common salt |
No change |
Neutral |
China Rose as Indicator
China rose is a natural indicator. It is called 'Gudhal' in Hindi. It is a light pink coloured solution which is extracted from the red flowers of China rose plant with water.
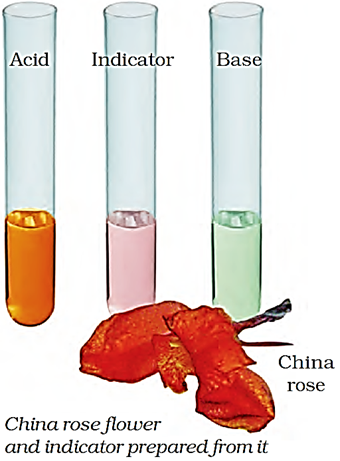
Activity 3 – To prepare China Rose Indicator
Collect some China rose petals and place them in a beaker and add some warm water. Keep the China rose petals immersed in water for some time till water in the beaker acquires a light pink colour. Remove the petals by filtration. The light pink solution thus obtained is the China rose indicator.
Effect of China rose indicator on different substances:
|
Test solution |
Initial colour |
Final colour |
|
Shampoo (dilute solution) |
White |
Green |
|
Lemon juice |
Colourless |
Deep pink (magenta) |
|
Soda water |
Colourless |
Pink |
|
Sodium hydrogen carbonate solution |
Colourless |
Green |
|
Vinegar |
Colourless |
Deep pink (magenta) |
|
Sugar solution |
Colourless |
No change |
|
Common salt solution |
Colourless |
No change |
Activity 4 – To demonstrate the effect on litmus paper, turmeric paper and China rose solution
Effect on litmus paper, turmeric paper and on China rose solution of different acidic and basic solution. Write the observation in tabular form.
|
Name of acid/base |
Effect on litmus paper |
Effect on turmeric paper |
Effect on China rose solution |
|
Dilute hydrochloric acid |
Blue to red |
Yellow |
Dark pink |
|
Sulphuric acid |
Blue to red |
Yellow |
Dark pink |
|
Nitric acid |
Blue to red |
Yellow |
Dark pink |
|
Acetic acid |
Blue to red |
Yellow |
Dark pink |
|
Sodium hydroxide |
Red to blue |
Red |
Green |
|
Ammonium hydroxide |
Red to blue |
Red |
Green |
|
Calcium hydroxide (lime water) |
Red to blue |
Red |
Green |
We observe that all three indicators give different results with acids, bases, and neutral solutions.
Acid Rain
The rain containing excess of acids called an acid rain. The rain becomes acidic because carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide dissolve in rain drops to form carbonic acid, sulphuric acid, and nitric acid respectively. It can cause damage to buildings, historical monuments, plants, and animals.
Effects of Acid Rain:
(i) Acid rain makes the water of lakes, ponds, and rivers too acidic due to which fish and other aquatic animals get killed.
(ii) Acid rain eats up the leaves of the trees gradually. By losing leaves, the trees die. Acid rain also damages crop plants in the fields.
(iii) Acid rain damages the metal structures like steel bridges, etc when it falls on them.
(iv) Acid rain damages the surfaces of buildings and monuments made up of marble.
Neutralisation
Acids and bases are chemically opposite substances. So, when an acid is mixed with a base, they neutralise (or cancel) the effect of each other. When an acid solution and a base solution are mixed in suitable amounts, both the acidic nature of the acid and the basic nature of the base are destroyed. The resulting solution is neither acidic nor basic. So, the reaction between an acid and base is known as neutralisation. In the process of neutralisation, salt and water are produced with the evolution of heat.
Salt produced in the reaction may be acidic, basic, or neutral in nature. The evolved heat raises the temperature of the reaction mixture.
Acid + Base → Salt + Water + (Heat is evolved)
e.g. HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
Hydrochloric acid Sodium hydroxide Sodium chloride Water
(Acid) (Base) (Salt)
Similarly, if dilute sulphuric acid is added to lime water (a base), then neutralisation reaction takes place and the reaction mixture becomes hot.
Activity 5: To show the effect of a synthetic indicator phenolphthalein on an acidic and basic solution.
We take small. amount of hydrochloric acid (5 ml) in a test tube. Solution of hydrochloric acid is colourless. Add 2-3 drops of phenolphthalein indicator to the acid in a test tube. Phenolphthalein indicator is colourless. Shake the test tube gently. There is no change in the colour of the acid.
Take sodium hydroxide solution in a dropper. Add this sodium hydroxide solution to hydrochloric acid in the test tube dropwise. Stir the tube gently. Continue to add sodium hydroxide solution drop by drop (while stirring) till a light pink colour just appears in the solution in the test tube. We then stop adding more of sodium hydroxide solution.
At this stage, all the hydrochloric acid in a test tube has been completely neutralised by sodium hydroxide solution. Thus, a neutralisation reaction has taken place in the test tube. If we add one more drop of dilute hydrochloric acid, then the solution again becomes colourless.

It is evident that when the solution is basic, phenolphthalein gives a pink colour and when the solution is acidic, it remains colourless.
If we again add one drop of sodium hydroxide solution in the test tube, the solution again becomes pink in colour. This is because now solution has excess of base which gives pink colour with phenolphthalein.
Neutralisations in Everyday Life
The neutralisation reactions involving acids and bases play a very important role in our everyday life. The treatment of an ant's sting, remedy for indigestion, soil treatment and the treatment of factory wastes, all involve neutralisation reaction.
Indigestion
Our stomach produces hydrochloric acid. This hydrochloric acid helps in digesting our food. Sometimes, excess of hydrochloric acid is produced in the stomach which causes indigestion. Due to indigestion, sometimes a person feels pain in the stomach and irritation. To relive indigestion, we take an antacid such as milk of magnesia. Milk of magnesia contains a base called magnesium hydroxide. Magnesium hydroxide neutralises the excess acid present in the stomach and cures indigestion. Another antacid is baking soda which contains a base sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Ant Bite
When an ant bites, it injects an acidic liquid into the skin of the person which causes burning pain. The sting of an ant contains an acid called formic acid. The effect of the acid can be neutralised by rubbing a mild base like baking soda solution (sodium hydrogen carbonate) or calamine solution. Calamine solution contains a base called zinc carbonate. Thus, being a base, baking soda solution or calamine solution neutralises the acidic liquid injected by the ant and cancels its effect.
Soil Treatment
The soil may be acidic or basic naturally. The plants do not grow well, if the soil at a place is too acidic or too basic. Excessive use of chemical fertilisers makes the soil acidic.
When the soil is too acidic, it is treated with bases like quicklime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide). These bases neutralise the excess acid present in the soil and reduce its acidic nature.
If the soil is basic, organic matter called manure or compost is added to it. The organic matter releases acids which neutralise the excess bases present in the soil and reduce its basic nature.
Factory Wastes
The waste substances discharged by many factories, contain acids. If these factory wastes are allowed to flow into the water bodies (like rivers, ponds, lakes, et c), then the acid present in them will kill fish and other organisms which live in the water bodies. The factory wastes are therefore neutralised by adding basic substances, e.g., slaked lime or quick lime, before discharging them into water bodies.
Online Tuitions & Self-Study Courses for Grade 6 to 12 & JEE / NEET
