Chapter 1 – Rational Numbers
NCERT Solutions
Exercise 1.1
Q.1. Using appropriate properties find:
Ans:
(i) 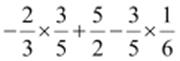
(ii) 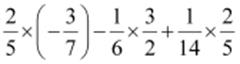
Ans:
(i) 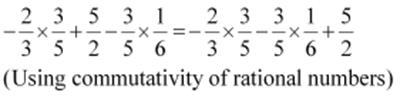
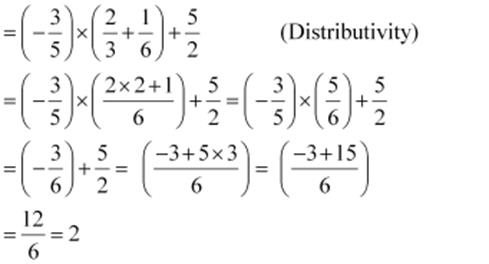
(ii) 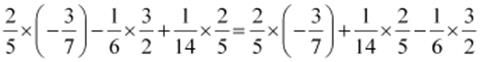 (By
commutativity)
(By
commutativity)

Q.2. Write the additive inverse of each of the following:
(i) 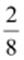 (ii)
(ii) 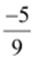 (iii)
(iii) 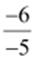 (iv)
(iv) 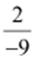 (v)
(v) 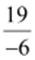
Ans:
(i) 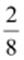
Additive
inverse = 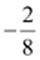
(ii) 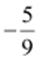
Additive
inverse = 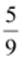
(iii) 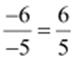
Additive
inverse = 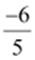
(iv) 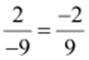
Additive
inverse 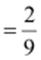
(v) 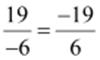
Additive
inverse 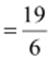
Q.3. Verify that −(−x) = x for.
(i) 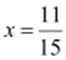 (ii)
(ii) 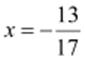
Ans:
(i) 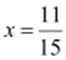
The
additive inverse of 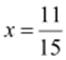 is
is 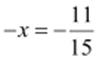 as
as 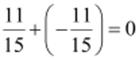
This
equality 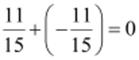 represents
that the additive inverse of
represents
that the additive inverse of 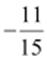 is
is 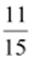 or
it can be said that
or
it can be said that 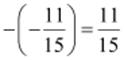 i.e.,
−(−x) = x
i.e.,
−(−x) = x
(ii) 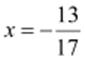
The
additive inverse of 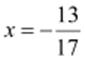 is
is 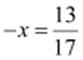 as
as 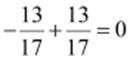
This
equality 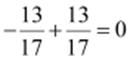 represents
that the additive inverse of
represents
that the additive inverse of 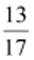 is
−
is
−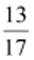 i.e.,
−(−x) = x
i.e.,
−(−x) = x
Q.4. Find the multiplicative inverse of the following.
(i) −13 (ii) 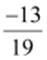 (iii)
(iii) 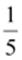
(iv) 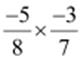 (v)
(v) 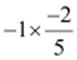 (vi)
−1
(vi)
−1
Ans:
(i) −13
Multiplicative
inverse = −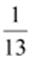
(ii) 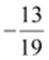
Multiplicative
inverse = 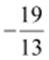
(iii) 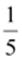
Multiplicative inverse = 5
(iv) 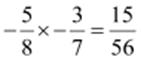
Multiplicative
inverse 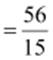
(v) 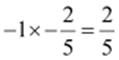
Multiplicative
inverse 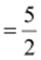
(vi) −1
Multiplicative inverse = −1
Q.5. Name the property under multiplication used in each of the following:
(i) 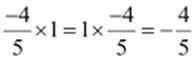
(ii) 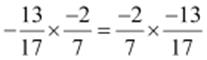
(iii) 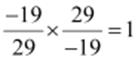
Ans:
(i) 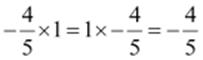
1 is the multiplicative identity.
(ii) Commutativity
(iii) Multiplicative inverse
Q.6. Multiply 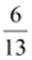 by
the reciprocal of
by
the reciprocal of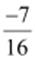 .
.
Ans:
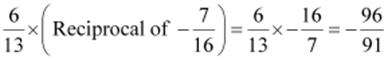
Q.7. Tell what property allows you to compute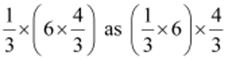 .
.
Ans: Associativity
Q.8. Is 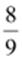 the
multiplicative inverse of
the
multiplicative inverse of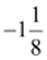 ?
Why or why not?
?
Why or why not?
Ans: If it is the multiplicative inverse, then the product should be 1.
However, here, the product is not 1 as
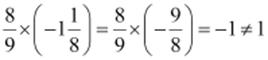
Q.9. Is 0.3 the multiplicative inverse of 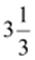 ?
Why or why not?
?
Why or why not?
Ans:
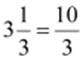
0.3
× 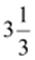 =
0.3 ×
=
0.3 × 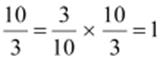
Here, the product is 1. Hence, 0.3
is the multiplicative inverse of 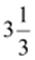 .
.
Q.10. Write:
(i) The rational number that does not have a reciprocal.
(ii) The rational numbers that are equal to their reciprocals.
(iii) The rational number that is equal to its negative.
Ans:
(i) 0 is a rational number but its reciprocal is not defined.
(ii) 1 and −1 are the rational numbers that are equal to their reciprocals.
(iii) 0 is the rational number that is equal to its negative.
Q.11. Fill in the blanks.
(i) Zero has __________ reciprocal.
(ii) The numbers __________ and __________ are their own reciprocals
(iii) The reciprocal of − 5 is __________.
(iv)
Reciprocal of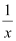 ,
where
,
where 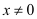 is
__________.
is
__________.
(v) The product of two rational numbers is always a __________.
(vi) The reciprocal of a positive rational number is __________.
Ans:
(i) No
(ii) 1, −1
(iii) 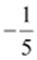
(iv) x
(v) Rational number
(vi) Positive rational number
Exercise 1.2
Q.1. Represent these numbers on the number line.
(i) 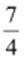 (ii)
(ii) 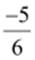
Ans:
(i) 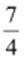 can
be represented on the number line as follows.
can
be represented on the number line as follows.
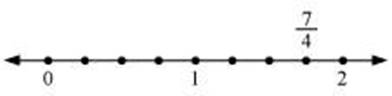
(ii) 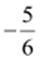 can
be represented on the number line as follows.
can
be represented on the number line as follows.
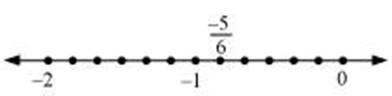
Q.2. Represent 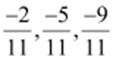 on
the number line.
on
the number line.
Ans:
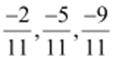 can be represented on the number line as follows.
can be represented on the number line as follows.
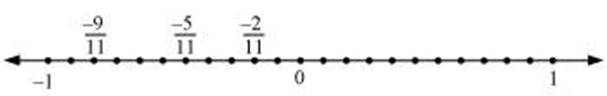
Q.3. Write five rational numbers which are smaller than 2.
Ans:
2 can be represented as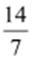 .
.
Therefore, five rational numbers smaller than 2 are
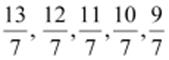
Q.4. Find ten rational numbers between 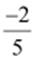 and
and
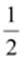 .
.
Ans:
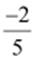 and
and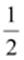 can
be represented as
can
be represented as 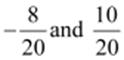 respectively.
respectively.
Therefore, ten rational numbers
between 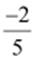 and
and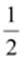 are
are
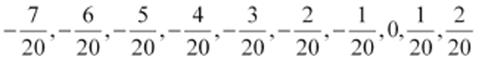
Q.5. Find five rational numbers between
(i) 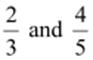
(ii) 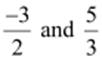
(iii) 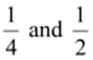
Ans:
(i) 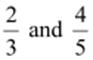 can
be represented as
can
be represented as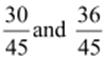 respectively.
respectively.
Therefore, five rational numbers
between 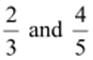 are
are
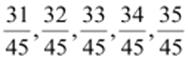
(ii) 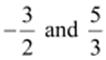 can
be represented as
can
be represented as 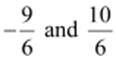 respectively.
respectively.
Therefore, five rational numbers
between 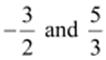 are
are
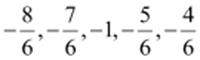
(iii) 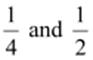 can
be represented as
can
be represented as 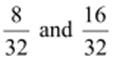 respectively.
respectively.
Therefore, five rational numbers
between 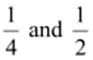 are
are
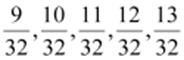
Q.6. Write five rational numbers greater than − 2.
Ans:
−2 can be represented as
−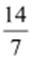 .
.
Therefore, five rational numbers greater than −2 are
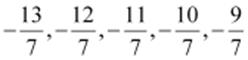
Q.7. Find ten rational numbers between 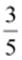 and
and
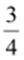 .
.
Ans:
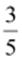 and
and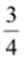 can
be represented as
can
be represented as 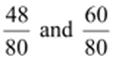 respectively.
respectively.
Therefore, ten rational numbers
between 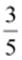 and
and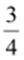 are
are
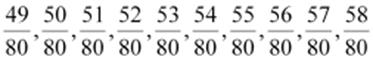
Online Tuitions & Self-Study Courses for Grade 6 to 12 & JEE / NEET
