Mensuration
Mensuration is the branch of mathematics that deals with the measurement of length, area or volume of various geometric shapes.
Perimeter
If we go around the figure along its boundary to form a closed figure then the distance covered is the perimeter of that figure. Hence the Perimeter refers to the length of the boundary of a closed figure.
If a figure is made up of line segments only then we can find its perimeter by adding the length of all the sides of the given figure.
Example
Find the Perimeter of the given figure.
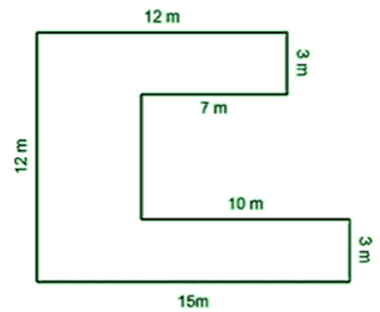
Solution
Perimeter = Sum of all the sides
= (12 + 3 + 7 + 6 + 10 + 3 + 15 + 12) m
= 68 m
- Perimeter of a circle is also called as the circumference of the circle.
Perimeter of a Triangle
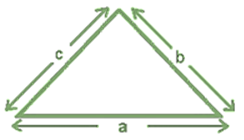
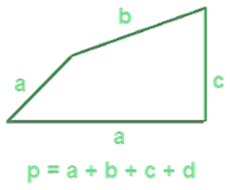
Perimeter of triangle = Sum of lengths of all sides = a + b + c.
- If
the given triangle is equilateral that is if all the sides are equal (a =
b = c),
then its perimeter is equal to 3 × length of one side of the triangle.
Perimeter of a Rectangle

Perimeter of the rectangle = length ( l ) + length ( l ) + width (w) + width (w)
= 2 × [length ( l ) + width (w)]
Example: 1
The length and breadth of a rectangular swimming pool are 16 and 12 meters respectively .find the perimeter of the pool.
Solution:
Perimeter of a rectangle = 2 × (length + breadth)
Perimeter of the pool = 2 × (16 + 12)
= 2 × 28
= 56 meters
Example: 2
Find the cost of fencing a rectangular farm of length 24 meters and breadth 18 meters at 8/- per meter.
Solution:
Perimeter of a rectangle = 2 × (length + breadth)
Perimeter of the farm = 2 × (24 + 18)
= 2 × 42
= 84 meter
Cost of fencing = 84 × 8
= Rs. 672
Thus, the cost of fencing the farm is Rs. 672/-.
Regular Closed Figure
Figures with equal length of sides and an equal measure of angles are known as Regular Closed Figures or Regular Polygon.
Perimeter of Regular Polygon = Number of sides × Length of one side
Perimeter of a Square
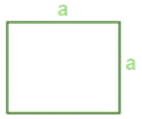
Perimeter of square = 4 × length of a side = 4a
Example
Find the perimeter of a square having side length 25 cm.
Solution
Perimeter of a square = 4 × length of a side
Perimeter of square = 4 × 25
= 100 cm
Perimeter of an Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle is a regular polygon with three equal sides and angles.
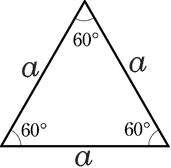
Perimeter of an equilateral triangle = 3 × length of a side
Example
Find the perimeter of a triangle having each side length 13 cm.
Solution
Perimeter of an equilateral triangle = 3 × length of a side
Perimeter of triangle = 3 × 13
= 39 cm
Perimeter of a Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon is a polygon with 5 equal sides and angles.

Perimeter of a regular pentagon = 5 × length of one side
Example
Find the perimeter of a pentagon having side length 9 cm.
Solution
Perimeter of a regular pentagon = 5 × length of one side
Perimeter of a regular pentagon = 5 × 9
= 45 cm
Perimeter of a Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon is a polygon with 6 equal sides and angles.
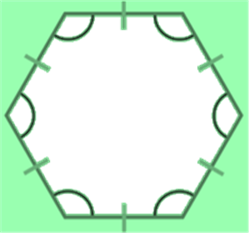
Perimeter of a regular hexagon = 6 × Length of one side
Example
Find the perimeter of a hexagon having side length 15cm.
Solution
Perimeter of a regular hexagon = 6 × Length of one side
Perimeter of a regular hexagon = 6 × 15
= 90 cm
Perimeter of a Regular Octagon
A regular octagon is a polygon with 8 equal sides and angles.
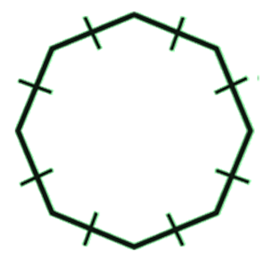
Perimeter of a regular octagon = 8 × length of one side
Example
Find the perimeter of an octagon having side length 7cm.
Solution
Perimeter of a regular octagon = 8 × length of one side
Perimeter of a regular octagon = 8 × 7
= 56 cm
Perimeter of a ‘n’ sided polygon
- A polygon is a closed shape made up of line segments.
- Perimeter of n sided polygon = n × length of one side.
- Example: Length of each side of a decagon is a
cm, then:
Perimeter of the decagon = 10a cm
Perimeter of irregular shapes
- Irregular shapes are the shapes which do not have all sides and angles equal.
- The
perimeter of irregular shapes is equal to total length covered by the
shape.
In the figure given below, perimeter is the sum of all sides.
Area
- Area is the total amount of surface enclosed by a closed figure.
- To find the area of any irregular closed figure, we can put them on a graph paper with the square of 1 cm × 1 cm .then estimate the area of that figure by counting the area of the squares covered by the figure.
- Here one square is taken as 1 sq.unit.
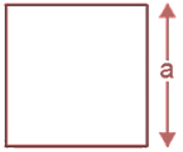
Area of Square
- Area of a square = Side × Side = Side2 = a2, where a is the length of each side.
Example
Calculate the area of a square of side 13 cm.
Solution
Area of a square = side × side
= 13 × 13
= 169 cm2.
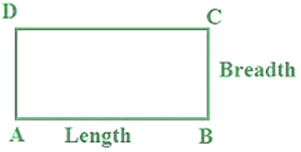
Area of Rectangle
- Area = length ( l ) × breadth ( b)
Example
Find the area of a rectangle whose length and breadth are 20 cm and 12 cm respectively.
Solution
Length of the rectangle = 20 cm
Breadth of the rectangle = 12 cm
Area of the rectangle = length × breadth
= 20 cm × 12 cm
= 240 sq cm.
Length of a rectangle if breadth and area are given:
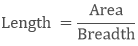
Example
What will be the length of the rectangle if its breadth is 6 m and the area is 48sq.m?
Solution
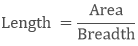
Length = 48/6
= 8 m
Breadth of the rectangle if length and area are given:
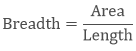
Example
What will be the breadth of the rectangle if its length is 8 m and the area is 81 sq.m?
Solution
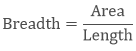
Breadth = 81/8
= 9 m
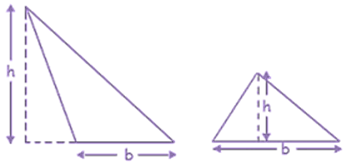
Area of a triangle
Area of triangle = (1/2) × base × height = (1/2) × b × h
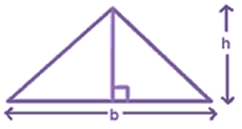
Areas of different types of triangles
- Consider
an acute and an obtuse triangle.
Area of each triangle = (1/2) × base × height = (1/2) × b × h
Visualisation of Area
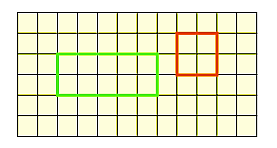
- In
the given graph, if the area of each small square is 1 cm2,
then
Area of rectangle = l × b = 5 × 2 = 10 cm2
Area of square = a × a = 2 × 2 = 4 cm2
Area of irregular shapes
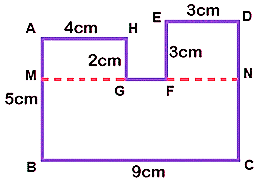
- Area
of an irregular figure can be calculated :
Step 1: Divide the irregular shape into regular shapes that you can recognize (eg. triangles, rectangles, circles and squares)
Step 2: Find the area of these individual shapes and add them. Sum will be the area of the irregular figure.
Example: Area of the given figure
= Area of MNCB + Area of AMGH + Area of EFND
= [ 5 × 9 + 4 × 2 + 3 × 3 ] cm2
= [45 + 8 + 9 ] cm2
= 62 cm2
Example
Find the area of the given figure. (1 square = 1 m2)
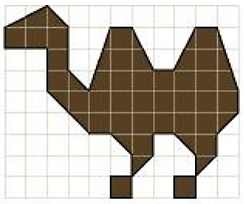
Solution
The given figure is made up of line segments and is covered with some full squares and some half squares.
Full squares in figure = 32
Half squares in figure = 21
Area covered by full squares = 32 × 1 sq. unit = 32 sq. unit.
Area covered by half squares = 21 × (1/2) sq. unit. = 10.5 sq. unit.
Total area covered by figure = 32 + 10.5 = 42.5 sq. unit.
